The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 amino acid sequence that engages tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factors is critical for primary B lymphocyte growth transformation
- PMID: 9037073
- PMCID: PMC19811
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.4.1447
The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 amino acid sequence that engages tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factors is critical for primary B lymphocyte growth transformation
Abstract
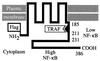
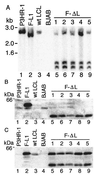
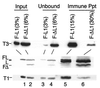
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) is essential for transforming primary B lymphocytes into lymphoblastoid cell lines. EBV recombinants with LMP1 genes truncated after the proximal 45 codons of the LMP1 carboxyl terminus are adequate for transformation. The proximal 45 residues include a domain that engages the tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factors (TRAFs). We investigated the importance of the TRAF binding domain by assaying the transforming ability of recombinant EBV genomes with a deletion of LMP1 codons 185-211. This mutation eliminates TRAF association in yeast and in lymphoblasts but does not affect LMP1 stability or localization. Specifically mutated recombinant EBV genomes were generated by transfecting P3HR-1 cells with overlapping EBV cosmids. Infection of primary B lymphocytes resulted in cell lines that were coinfected with an LMP1 delta185-211 EBV recombinant and P3HR-1 EBV, which has a wild-type LMP1 gene but is transformation defective due to another deletion. Despite the equimolar mixture of wild-type and mutated LMP1 genes in virus preparations from five coinfected cell lines, only the wild-type LMP1 gene was found in 412 cell lines obtained after transformation of primary B lymphocytes. No transformed cell line had only the LMP1 delta185-211 gene. An EBV recombinant with a Flag-tagged LMP1 gene passaged in parallel segregated from the coinfecting P3HR-1. These data indicate that the LMP1 TRAF binding domain is critical for primary B lymphocyte growth transformation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The residues between the two transformation effector sites of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 are not critical for B-lymphocyte growth transformation.J Virol. 1999 Dec;73(12):9908-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.12.9908-9916.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10559303 Free PMC article.
-
Association of TRAF1, TRAF2, and TRAF3 with an Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 domain important for B-lymphocyte transformation: role in NF-kappaB activation.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Dec;16(12):7098-108. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.12.7098. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8943365 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 cytoplasmic carboxy terminus is essential for B-lymphocyte transformation; fibroblast cocultivation complements a critical function within the terminal 155 residues.J Virol. 1995 Feb;69(2):675-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.69.2.675-683.1995. J Virol. 1995. PMID: 7815530 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-barr virus transformation: involvement of latent membrane protein 1-mediated activation of NF-kappaB.Oncogene. 1999 Nov 22;18(49):6959-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203217. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10602470 Review.
-
The role of Epstein-Barr virus in neoplastic transformation.Oncology. 2001;60(4):289-302. doi: 10.1159/000058523. Oncology. 2001. PMID: 11408795 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 is critical for latent membrane protein 1-induced p65/RelA serine 536 phosphorylation and NF-kappaB activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Feb 21;103(8):2689-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0511096103. Epub 2006 Feb 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16477006 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A alters in vivo and in vitro models of B-cell anergy, but not deletion, in response to autoantigen.J Virol. 2005 Jun;79(12):7355-62. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7355-7362.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15919890 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-transforming protein latent infection membrane protein 1 activates transcription factor NF-kappaB through a pathway that includes the NF-kappaB-inducing kinase and the IkappaB kinases IKKalpha and IKKbeta.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Aug 18;95(17):10106-11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.17.10106. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9707608 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein-Barr virus oncogene product latent membrane protein 1 engages the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated death domain protein to mediate B lymphocyte growth transformation and activate NF-kappaB.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Nov 11;94(23):12592-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.23.12592. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9356494 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of latent membrane protein 1 impairs the growth and tumorigenesis of latency II Epstein-Barr virus-transformed T cells.J Virol. 2012 Apr;86(7):3934-43. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05747-11. Epub 2012 Jan 18. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22258264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rickinson A B, Kieff E. In: Virology. Fields B N, Knipe D M, Howley P M, Chanock R M, Melnick J L, Monath T P, Roizman B, Straus S, editors. Philadelphia: Raven; 1996. pp. 2397–2446.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

