Cardiac Fibroblastic Niches in Homeostasis and Inflammation
- PMID: 38843287
- PMCID: PMC11149942
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.124.323892
Cardiac Fibroblastic Niches in Homeostasis and Inflammation
Abstract
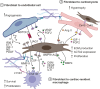
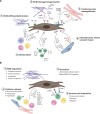
Fibroblasts are essential for building and maintaining the structural integrity of all organs. Moreover, fibroblasts can acquire an inflammatory phenotype to accommodate immune cells in specific niches and to provide migration, differentiation, and growth factors. In the heart, balancing of fibroblast activity is critical for cardiac homeostasis and optimal organ function during inflammation. Fibroblasts sustain cardiac homeostasis by generating local niche environments that support housekeeping functions and by actively engaging in intercellular cross talk. During inflammatory perturbations, cardiac fibroblasts rapidly switch to an inflammatory state and actively communicate with infiltrating immune cells to orchestrate immune cell migration and activity. Here, we summarize the current knowledge on the molecular landscape of cardiac fibroblasts, focusing on their dual role in promoting tissue homeostasis and modulating immune cell-cardiomyocyte interaction. In addition, we discuss potential future avenues for manipulating cardiac fibroblast activity during myocardial inflammation.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; endothelial cells; fibroblasts; homeostasis; inflammation; myocarditis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heart-infiltrating prominin-1+/CD133+ progenitor cells represent the cellular source of transforming growth factor beta-mediated cardiac fibrosis in experimental autoimmune myocarditis.Circ Res. 2009 Aug 28;105(5):462-70. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.196287. Epub 2009 Jul 23. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19628793
-
The development of myocardial fibrosis in transgenic mice with targeted overexpression of tumor necrosis factor requires mast cell-fibroblast interactions.Circulation. 2011 Nov 8;124(19):2106-16. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.052399. Epub 2011 Oct 24. Circulation. 2011. PMID: 22025605 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac intercellular communication: are myocytes and fibroblasts fair-weather friends?J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2012 Dec;5(6):768-82. doi: 10.1007/s12265-012-9404-5. Epub 2012 Sep 27. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2012. PMID: 23015462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac fibroblasts recruit Th17 cells infiltration into myocardium by secreting CCL20 in CVB3-induced acute viral myocarditis.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32(5):1437-50. doi: 10.1159/000356581. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013. PMID: 24296428
-
Role of inflammatory cells in fibroblast activation.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016 Apr;93:143-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.11.016. Epub 2015 Nov 20. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26593723 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac fibroblasts: answering the call.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024 Sep 1;327(3):H681-H686. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00478.2024. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39093000 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McLellan MA, Skelly DA, Dona MSI, Squiers GT, Farrugia GE, Gaynor TL, Cohen CD, Pandey R, Diep H, Vinh A, et al. . High-resolution transcriptomic profiling of the heart during chronic stress reveals cellular drivers of cardiac fibrosis and hypertrophy. Circulation. 2020;142:1448–1463. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.045115 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Perez-Shibayama C, Gil-Cruz C, Cadosch N, Lütge M, Cheng HW, De Martin A, Frischmann K, Joachimbauer A, Onder L, Papadopoulou I, et al. . Bone morphogenic protein-4 availability in the cardiac microenvironment controls inflammation and fibrosis in autoimmune myocarditis. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2024;3:301–316. doi: 10.1038/s44161-024-00432-0
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

