Human skeletal muscle aging atlas
- PMID: 38622407
- PMCID: PMC11108788
- DOI: 10.1038/s43587-024-00613-3
Human skeletal muscle aging atlas
Abstract
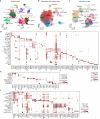
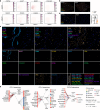
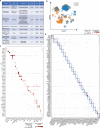
Skeletal muscle aging is a key contributor to age-related frailty and sarcopenia with substantial implications for global health. Here we profiled 90,902 single cells and 92,259 single nuclei from 17 donors to map the aging process in the adult human intercostal muscle, identifying cellular changes in each muscle compartment. We found that distinct subsets of muscle stem cells exhibit decreased ribosome biogenesis genes and increased CCL2 expression, causing different aging phenotypes. Our atlas also highlights an expansion of nuclei associated with the neuromuscular junction, which may reflect re-innervation, and outlines how the loss of fast-twitch myofibers is mitigated through regeneration and upregulation of fast-type markers in slow-twitch myofibers with age. Furthermore, we document the function of aging muscle microenvironment in immune cell attraction. Overall, we present a comprehensive human skeletal muscle aging resource ( https://www.muscleageingcellatlas.org/ ) together with an in-house mouse muscle atlas to study common features of muscle aging across species.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
In the past 3 years, S.A.T. has consulted for or been a member of scientific advisory boards at Qiagen, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline and ForeSite Labs. She is a co-founder and an equity holder of TransitionBio and EnsoCell and a SAB member of Element Biosciences. She is a part-time employee at GlaxoSmithKline. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Deletion of Pofut1 in Mouse Skeletal Myofibers Induces Muscle Aging-Related Phenotypes in cis and in trans.Mol Cell Biol. 2017 May 2;37(10):e00426-16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00426-16. Print 2017 May 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28265002 Free PMC article.
-
Destabilization of the neuromuscular junction by proteolytic cleavage of agrin results in precocious sarcopenia.FASEB J. 2011 Dec;25(12):4378-93. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-191262. Epub 2011 Sep 1. FASEB J. 2011. PMID: 21885656
-
A robust neuromuscular system protects rat and human skeletal muscle from sarcopenia.Aging (Albany NY). 2016 Apr;8(4):712-29. doi: 10.18632/aging.100926. Aging (Albany NY). 2016. PMID: 27019136 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiology and mechanisms of primary sarcopenia (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2021 Aug;48(2):156. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4989. Epub 2021 Jun 29. Int J Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34184088 Review.
-
Sarcopenia: Aging-Related Loss of Muscle Mass and Function.Physiol Rev. 2019 Jan 1;99(1):427-511. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00061.2017. Physiol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30427277 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unlocking the potential of exercise: harnessing myokines to delay musculoskeletal aging and improve cognitive health.Front Physiol. 2024 Sep 2;15:1338875. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1338875. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39286235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calorie restriction and rapamycin distinctly mitigate aging-associated protein phosphorylation changes in mouse muscles.Commun Biol. 2024 Aug 10;7(1):974. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06679-4. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39127848 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of MAT2A Impairs Skeletal Muscle Repair Function.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 2;14(9):1098. doi: 10.3390/biom14091098. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334864 Free PMC article.
-
Aging atlas reveals cell-type-specific effects of pro-longevity strategies.Nat Aging. 2024 Jul;4(7):998-1013. doi: 10.1038/s43587-024-00631-1. Epub 2024 May 30. Nat Aging. 2024. PMID: 38816550 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated multi-omic analyses uncover the effects of aging on cell-type regulation in glucose-responsive tissues.Aging Cell. 2024 Aug;23(8):e14199. doi: 10.1111/acel.14199. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Aging Cell. 2024. PMID: 38932492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Falls. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/falls (2021).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- WT211276/Z/18/Z/Wellcome Trust (Wellcome)
- 101026233/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 2021A1515012065/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Guangdong Natural Science Foundation)
- 220540/Z/20/A/Wellcome Trust (Wellcome)
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

