Satellite RNAs: emerging players in subnuclear architecture and gene regulation
- PMID: 37526230
- PMCID: PMC10505914
- DOI: 10.15252/embj.2023114331
Satellite RNAs: emerging players in subnuclear architecture and gene regulation
Abstract
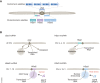
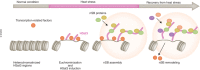
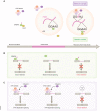
Satellite DNA is characterized by long, tandemly repeated sequences mainly found in centromeres and pericentromeric chromosomal regions. The recent advent of telomere-to-telomere sequencing data revealed the complete sequences of satellite regions, including centromeric α-satellites and pericentromeric HSat1-3, which together comprise ~ 5.7% of the human genome. Despite possessing constitutive heterochromatin features, these regions are transcribed to produce long noncoding RNAs with highly repetitive sequences that associate with specific sets of proteins to play various regulatory roles. In certain stress or pathological conditions, satellite RNAs are induced to assemble mesoscopic membraneless organelles. Specifically, under heat stress, nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) are scaffolded by HSat3 lncRNAs, which sequester hundreds of RNA-binding proteins. Upon removal of the stressor, nSBs recruit additional regulatory proteins, including protein kinases and RNA methylases, which modify the previously sequestered nSB components. The sequential recruitment of substrates and enzymes enables nSBs to efficiently regulate the splicing of hundreds of pre-mRNAs under limited temperature conditions. This review discusses the structural features and regulatory roles of satellite RNAs in intracellular architecture and gene regulation.
Keywords: T2T genome; membraneless organelle; noncoding RNA; satellite DNA; stress response.
© 2023 The Authors. Published under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pericentromeric satellite RNAs as flexible protein partners in the regulation of nuclear structure.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2024 Jul-Aug;15(4):e1868. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1868. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2024. PMID: 38973000 Review.
-
Transcription of tandemly repetitive DNA: functional roles.Chromosome Res. 2015 Sep;23(3):463-77. doi: 10.1007/s10577-015-9494-4. Chromosome Res. 2015. PMID: 26403245 Review.
-
Two distinct nuclear stress bodies containing different sets of RNA-binding proteins are formed with HSATIII architectural noncoding RNAs upon thermal stress exposure.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Aug 20;516(2):419-423. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.06.061. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 31227213
-
Accumulation of small murine minor satellite transcripts leads to impaired centromeric architecture and function.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jun 6;103(23):8709-14. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508006103. Epub 2006 May 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16731634 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional characterization of noncoding repetitive RNAs transcribed in stressed human cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Jun;16(6):2597-604. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-12-1078. Epub 2005 Mar 23. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15788562 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Answering the Cell Stress Call: Satellite Non-Coding Transcription as a Response Mechanism.Biomolecules. 2024 Jan 17;14(1):124. doi: 10.3390/biom14010124. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38254724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exceptionally long-lived nuclear RNAs.Science. 2024 Apr 5;384(6691):31-32. doi: 10.1126/science.ado5751. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Science. 2024. PMID: 38574156 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic ETS fusions promote DNA damage and proinflammatory responses via pericentromeric RNAs in extracellular vesicles.J Clin Invest. 2024 Mar 26;134(9):e169470. doi: 10.1172/JCI169470. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38530366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altemose N (2022) A classical revival: Human satellite DNAs enter the genomics era. Semin Cell Dev Biol 128: 2–14 - PubMed
-
- Aly MK, Ninomiya K, Adachi S, Natsume T, Hirose T (2019) Two distinct nuclear stress bodies containing different sets of RNA‐binding proteins are formed with HSATIII architectural noncoding RNAs upon thermal stress exposure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 516: 419–423 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

