The Beneficial Effects of Lactobacillus GG Therapy on Liver and Drinking Assessments in Patients with Moderate Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis
- PMID: 37040544
- PMCID: PMC10524173
- DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002283
The Beneficial Effects of Lactobacillus GG Therapy on Liver and Drinking Assessments in Patients with Moderate Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis
Abstract
Introduction: We investigated the effect of daily oral Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) in reducing liver injury/severity and drinking in patients with alcohol use disorder and moderately severe alcohol-associated hepatitis.
Methods: Forty-six male and female individuals with alcohol use disorder and moderate alcohol-associated hepatitis (12 ≤ model for end-stage liver disease score < 20, aged 21-67 years) received either LGG (n = 24) or placebo (n = 22). Data were collected/assessed at baseline and at 1, 3, and 6 months.
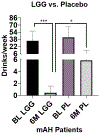
Results: LGG treatment was associated with a significant reduction in liver injury after 1 month. Six months of LGG treatment reduced heavy drinking levels to social or abstinence levels.
Discussion: LGG treatment was associated with an improvement in both liver injury and drinking.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01922895.
Copyright © 2023 by The American College of Gastroenterology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
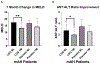
Similar articles
-
Lactobacillus GG treatment ameliorates alcohol-induced intestinal oxidative stress, gut leakiness, and liver injury in a rat model of alcoholic steatohepatitis.Alcohol. 2009 Mar;43(2):163-72. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2008.12.009. Alcohol. 2009. PMID: 19251117 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus rhamnosus Granules Dose-Dependently Balance Intestinal Microbiome Disorders and Ameliorate Chronic Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury.J Med Food. 2020 Feb;23(2):114-124. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2018.4357. Epub 2019 Nov 20. J Med Food. 2020. PMID: 31747353
-
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG reduces hepatic TNFα production and inflammation in chronic alcohol-induced liver injury.J Nutr Biochem. 2013 Sep;24(9):1609-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.02.001. Epub 2013 Apr 22. J Nutr Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23618528 Free PMC article.
-
Health benefits of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Bifidobacterium animalis subspecies lactis BB-12 in children.Postgrad Med. 2020 Jun;132(5):441-451. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2020.1731214. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Postgrad Med. 2020. PMID: 32059116 Review.
-
Alcoholic hepatitis: Towards an era of personalised management.United European Gastroenterol J. 2020 Nov;8(9):995-1002. doi: 10.1177/2050640620945886. Epub 2020 Jul 27. United European Gastroenterol J. 2020. PMID: 32718222 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in the management of alcohol-associated liver disease.Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2024 Nov 5;12:goae097. doi: 10.1093/gastro/goae097. eCollection 2024. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2024. PMID: 39502523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of efficacy and safety of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LRa05 in the eradication of Helicobacter pylori: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 21;15:1450414. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1450414. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39234246 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Gut Bacteria in Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease.Clin Liver Dis. 2024 Nov;28(4):663-679. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2024.06.008. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Clin Liver Dis. 2024. PMID: 39362714 Review.
-
Alcohol-associated liver disease.J Clin Invest. 2024 Feb 1;134(3):e176345. doi: 10.1172/JCI176345. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38299591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunological mechanisms in steatotic liver diseases: An overview and clinical perspectives.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024 Oct;30(4):620-648. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0315. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38988278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Szabo G and Lippai D, Converging actions of alcohol on liver and brain immune signaling. International review of neurobiology, 2014. 118: p. 359–380. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt C, Thinking from the Gut. Nature, 2015. 518(7540): p. S12–S14. - PubMed
-
- Crabb DW, et al., Diagnosis and Treatment of Alcohol-Associated Liver Diseases: 2019 Practice Guidance From the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology, 2020. 71(1): p. 306–333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

