CD69-oxLDL ligand engagement induces Programmed Cell Death 1 (PD-1) expression in human CD4 + T lymphocytes
- PMID: 35930205
- PMCID: PMC9355928
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-022-04481-1
CD69-oxLDL ligand engagement induces Programmed Cell Death 1 (PD-1) expression in human CD4 + T lymphocytes
Abstract
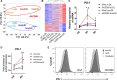
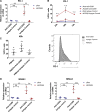
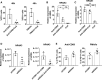
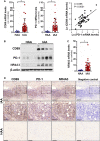
The mechanisms that control the inflammatory-immune response play a key role in tissue remodelling in cardiovascular diseases. T cell activation receptor CD69 binds to oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL), inducing the expression of anti-inflammatory NR4A nuclear receptors and modulating inflammation in atherosclerosis. To understand the downstream T cell responses triggered by the CD69-oxLDL binding, we incubated CD69-expressing Jurkat T cells with oxLDL. RNA sequencing revealed a differential gene expression profile dependent on the presence of CD69 and the degree of LDL oxidation. CD69-oxLDL binding induced the expression of NR4A receptors (NR4A1 and NR4A3), but also of PD-1. These results were confirmed using oxLDL and a monoclonal antibody against CD69 in CD69-expressing Jurkat and primary CD4 + lymphocytes. CD69-mediated induction of PD-1 and NR4A3 was dependent on NFAT activation. Silencing NR4A3 slightly increased PD-1 levels, suggesting a potential regulation of PD-1 by this receptor. Moreover, expression of PD-1, CD69 and NR4A3 was increased in human arteries with chronic inflammation compared to healthy controls, with a strong correlation between PD-1 and CD69 mRNA expression (r = 0.655 P < 0.0001). Moreover, PD-1 was expressed in areas enriched in CD3 infiltrating T cells. Our results underscore a novel mechanism of PD-1 induction independent of TCR signalling that might contribute to the role of CD69 in the modulation of inflammation and vascular remodelling in cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory response; CD69 leucocyte activation receptor; Cardiovascular disease; Inflamed aorta; Programmed Death 1 (PD-1); oxLDL.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unraveling CD69 signaling pathways, ligands and laterally associated molecules.EXCLI J. 2023 Mar 16;22:334-351. doi: 10.17179/excli2022-5751. eCollection 2023. EXCLI J. 2023. PMID: 37223078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidized low-density lipoproteins activate CD4+ T cell apoptosis in patients with end-stage renal disease through Fas engagement.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007 Jan;18(1):331-42. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2006050514. Epub 2006 Dec 20. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007. Retraction in: J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 Mar;25(3):645. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2014010004 PMID: 17182885 Retracted.
-
Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor in Lymphocytes Prevents Atherosclerosis and Predicts Subclinical Disease.Circulation. 2019 Jan 8;139(2):243-255. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.034326. Circulation. 2019. PMID: 30586697
-
Monocytes influence the fate of T cells challenged with oxidised low density lipoproteins towards apoptosis or MHC-restricted proliferation.Atherosclerosis. 2001 May;156(1):11-21. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(00)00575-x. Atherosclerosis. 2001. PMID: 11368992
-
CD4+ T cells in inflammatory diseases: pathogenic T-helper cells and the CD69-Myl9 system.Int Immunol. 2021 Nov 25;33(12):699-704. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxab053. Int Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34427648 Review.
Cited by
-
Leukemic cell-secreted interleukin-9 suppresses cytotoxic T cell-mediated killing in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Feb 15;15(2):144. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06528-6. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38360867 Free PMC article.
-
CD69 is a Promising Immunotherapy and Prognosis Prediction Target in Cancer.Immunotargets Ther. 2024 Jan 9;13:1-14. doi: 10.2147/ITT.S439969. eCollection 2024. Immunotargets Ther. 2024. PMID: 38223406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling CD69 signaling pathways, ligands and laterally associated molecules.EXCLI J. 2023 Mar 16;22:334-351. doi: 10.17179/excli2022-5751. eCollection 2023. EXCLI J. 2023. PMID: 37223078 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sancho D, Gómez M, Viedma F, Esplugues E, Gordón-Alonso M, Angeles García-López M, de la Fuente H, Martínez-A C, Lauzurica P, Sánchez-Madrid F. CD69 downregulates autoimmune reactivity through active transforming growth factor-β production in collagen-induced arthritis. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:872–882. doi: 10.1172/JCI200319112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

