Serum levels of IL-37 and correlation with inflammatory cytokines and clinical outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease
- PMID: 35636779
- PMCID: PMC9726976
- DOI: 10.1136/jim-2021-002134
Serum levels of IL-37 and correlation with inflammatory cytokines and clinical outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease
Abstract
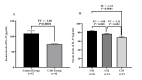
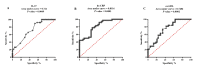
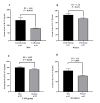
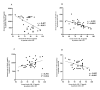
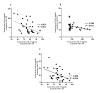
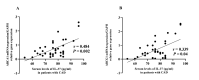
Coronary artery disease (CAD) due to atherosclerosis is one of the important reasons for death worldwide. Recent evidence has suggested the essential role of inflammation in the progression of atherosclerosis. Interleukin (IL)-37 is a critical anti-inflammatory member of the IL-1 family which regulates the inflammatory processes. The aim of this study was to compare the serum levels of IL-37 in patients with CAD compared with the control group and its correlation with oxidative stress, cholesterol homeostasis, and inflammation in patients with CAD. A total of 42 patients with CAD and 42 sex-matched and age- matched controls who underwent coronary angiography were included in this study. The serum levels of IL-37 were evaluated via ELISA. Serum levels of biochemical risk factors were determined by enzymatic methods. Serum levels of IL-37 in the CAD group subjects were significantly lower than in the control group and IL-37 was significantly increased in men with CAD than in women with CAD. IL-37 significantly had an inverse correlation with IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-32, high-sensitivity C reactive protein, oxidized low-density lipoprotein, and malondialdehyde. Also, IL-37 had a significantly positive correlation with ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay. In addition, IL-37 has positively correlated with ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 and G1 gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and serum levels of the FRAP. A receiver operating characteristic test displayed that IL-37 level ratios were a relatively significant CAD predictor. Our results indicated that decreased serum levels of IL-37 in patients with CAD and its relationship with inflammatory cytokines and reverse cholesterol transport genes are more likely to be associated in the inflammatory process with disease pathology.
Keywords: coronary artery disease; cytokines; inflammation; interleukins; tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
© American Federation for Medical Research 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Serum Levels of IL-36 in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease and Their Correlation with the Serum Levels of IL-32, IL-6, TNF-α, and Oxidative Stress.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2022;183(10):1137-1145. doi: 10.1159/000525845. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35878588
-
Expression levels of miR-27a, miR-329, ABCA1, and ABCG1 genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and their correlation with serum levels of oxidative stress and hs-CRP in the patients with coronary artery disease.IUBMB Life. 2021 Jan;73(1):223-237. doi: 10.1002/iub.2421. Epub 2020 Dec 1. IUBMB Life. 2021. PMID: 33263223
-
Lower Expression of miR-10a in Coronary Artery Disease and its Association with Pro/Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines.Clin Lab. 2018 May 1;64(5):847-854. doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2018.171222. Clin Lab. 2018. PMID: 29739060
-
Fibrinogen and a Triad of Thrombosis, Inflammation, and the Renin-Angiotensin System in Premature Coronary Artery Disease in Women: A New Insight into Sex-Related Differences in the Pathogenesis of the Disease.Biomolecules. 2021 Jul 15;11(7):1036. doi: 10.3390/biom11071036. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34356659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hegemony of inflammation in atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 5;966:176338. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176338. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38242225 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-6 and uric acid among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with coronary artery disease.Bioinformation. 2023 Dec 31;19(12):1134-1138. doi: 10.6026/973206300191134. eCollection 2023. Bioinformation. 2023. PMID: 38250529 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the role of CCL4-CCR5 in coronary artery disease pathogenesis: insights from Mendelian randomization, bulk RNA sequencing, single-cell RNA, and clinical validation.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Oct 14;21(14):2683-2693. doi: 10.7150/ijms.99518. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39512689 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased plasma miR-140-3p is associated with coronary artery disease.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 25;10(5):e26960. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26960. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38444486 Free PMC article.
-
IL‑37 suppresses macrophage ferroptosis to attenuate diabetic atherosclerosis via the NRF2 pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2023 May 3;25(6):289. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.11988. eCollection 2023 Jun. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37206550 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of Serum Oxidative and Antioxidative Status in Congenital Central Hypoventilation Syndrome (CCHS) Patients.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 30;11(8):1497. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081497. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009216 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohmmad‐Rezaei M, Arefnezhad R, Ahmadi R, et al. . An overview of the innate and adaptive immune system in atherosclerosis. IUBMB Life 2021;73:64–91. 10.1002/iub.2425 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

