The origins and roles of osteoclasts in bone development, homeostasis and repair
- PMID: 35502779
- PMCID: PMC9124578
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.199908
The origins and roles of osteoclasts in bone development, homeostasis and repair
Abstract
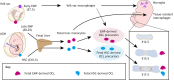
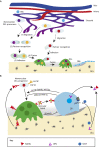
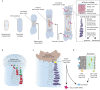
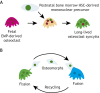
The mechanisms underlying bone development, repair and regeneration are reliant on the interplay and communication between osteoclasts and other surrounding cells. Osteoclasts are multinucleated monocyte lineage cells with resorptive abilities, forming the bone marrow cavity during development. This marrow cavity, essential to hematopoiesis and osteoclast-osteoblast interactions, provides a setting to investigate the origin of osteoclasts and their multi-faceted roles. This Review examines recent developments in the embryonic understanding of osteoclast origin, as well as interactions within the immune environment to regulate normal and pathological bone development, homeostasis and repair.
Keywords: Bone development; Hematopoietic stem cell; Osteoclast; Yolk sac.
© 2022. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Osteoclast 121F antigen expression during osteoblast conditioned medium induction of osteoclast-like cells in vitro: relationship to calcitonin responsiveness, tartrate resistant acid phosphatase levels, and bone resorptive activity.J Bone Miner Res. 1995 Jan;10(1):45-58. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650100109. J Bone Miner Res. 1995. PMID: 7747630
-
Erythromyeloid progenitors give rise to a population of osteoclasts that contribute to bone homeostasis and repair.Nat Cell Biol. 2020 Jan;22(1):49-59. doi: 10.1038/s41556-019-0437-8. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Nat Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 31907410 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation and function of osteoclasts.Keio J Med. 2003 Mar;52(1):1-7. doi: 10.2302/kjm.52.1. Keio J Med. 2003. PMID: 12713016 Review.
-
Interaction between osteoblast and osteoclast: impact in bone disease.Histol Histopathol. 2004 Oct;19(4):1325-44. doi: 10.14670/HH-19.1325. Histol Histopathol. 2004. PMID: 15375775 Review.
-
The Role Of BMPs in the Regulation of Osteoclasts Resorption and Bone Remodeling: From Experimental Models to Clinical Applications.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 26;13:869422. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.869422. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35558080 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Origin of Osteoclasts: Osteoclast Precursor Cells.J Bone Metab. 2023 May;30(2):127-140. doi: 10.11005/jbm.2023.30.2.127. Epub 2023 May 31. J Bone Metab. 2023. PMID: 37449346 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of ZC4H2, an Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita Associated Gene, Promotes Osteoclastogenesis in Mice.Genes (Basel). 2024 Aug 28;15(9):1134. doi: 10.3390/genes15091134. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39336725 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoclast differentiation and dynamic mRNA expression during mice embryonic palatal bone development.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 13;13(1):15170. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42423-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37704707 Free PMC article.
-
Naked cuticle homolog 2 controls the differentiation of osteoblasts and osteoclasts and ameliorates bone loss in ovariectomized mice.Genes Dis. 2024 Jan 12;12(1):101209. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101209. eCollection 2025 Jan. Genes Dis. 2024. PMID: 39552785 Free PMC article.
-
Osteogenesis imperfecta type 10 and the cellular scaffolds underlying common immunological diseases.Genes Immun. 2024 Aug;25(4):265-276. doi: 10.1038/s41435-024-00277-4. Epub 2024 May 29. Genes Immun. 2024. PMID: 38811682 Review.
References
-
- Arai, F., Miyamoto, T., Ohneda, O., Inada, T., Sudo, T., Brasel, K., Miyata, T., Anderson, D. M. and Suda, T. (1999). Commitment and differentiation of osteoclast precursor cells by the sequential expression of c-Fms and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB (RANK) receptors. J. Exp. Med. 190, 1741-1754. 10.1084/jem.190.12.1741 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

