Conditional loss of IKKα in Osterix + cells has no effect on bone but leads to age-related loss of peripheral fat
- PMID: 35318397
- PMCID: PMC8940989
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-08914-6
Conditional loss of IKKα in Osterix + cells has no effect on bone but leads to age-related loss of peripheral fat
Abstract
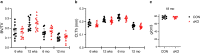
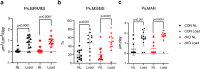
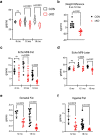
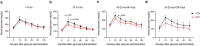
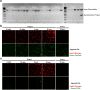
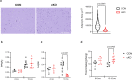
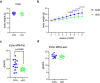
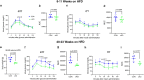
NF-κB has been reported to both promote and inhibit bone formation. To explore its role in osteolineage cells, we conditionally deleted IKKα, an upstream kinase required for non-canonical NF-κB activation, using Osterix (Osx)-Cre. Surprisingly, we found no effect on either cancellous or cortical bone, even following mechanical loading. However, we noted that IKKα conditional knockout (cKO) mice began to lose body weight after 6 months of age with severe reductions in fat mass and lower adipocyte size in geriatric animals. qPCR analysis of adipogenic markers in fat pads of cKO mice indicated no difference in early differentiation, but instead markedly lower leptin with age. We challenged young mice with a high fat diet finding that cKO mice gained less weight and showed improved glucose metabolism. Low levels of recombination at the IKKα locus were detected in fat pads isolated from old cKO mice. To determine whether recombination occurs in adipocytes, we examined fat pads in Osx-Cre;TdT reporter mice; these showed increasing Osx-Cre-mediated expression in peripheral adipocytes from 6 weeks to 18 months. Since Osx-Cre drives recombination in peripheral adipocytes with age, we conclude that fat loss in cKO mice is most likely caused by progressive deficits of IKKα in adipocytes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Conditional Activation of NF-κB Inducing Kinase (NIK) in the Osteolineage Enhances Both Basal and Loading-Induced Bone Formation.J Bone Miner Res. 2019 Nov;34(11):2087-2100. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3819. Epub 2019 Jul 31. J Bone Miner Res. 2019. PMID: 31246323 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of PPARγ in Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Does not Prevent High-Fat Diet-Induced Bone Deterioration in Mice.J Nutr. 2021 Sep 4;151(9):2697-2704. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxab173. J Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34113980 Free PMC article.
-
VEGFA From Early Osteoblast Lineage Cells (Osterix+) Is Required in Mice for Fracture Healing.J Bone Miner Res. 2019 Sep;34(9):1690-1706. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3755. Epub 2019 Aug 1. J Bone Miner Res. 2019. PMID: 31081125 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional disruption of the prolyl hydroxylase domain-containing protein 2 (Phd2) gene defines its key role in skeletal development.J Bone Miner Res. 2014 Oct;29(10):2276-86. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2258. J Bone Miner Res. 2014. PMID: 24753072
-
Mechanisms involved in bone resorption regulated by vitamin D.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Mar;177:70-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Nov 14. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29146302 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of bone homeostasis: signaling pathways and therapeutic targets.MedComm (2020). 2024 Jul 24;5(8):e657. doi: 10.1002/mco2.657. eCollection 2024 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39049966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Regulation of Osteoclastogenesis and Osteoblastogenesis.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2023 Oct;38(5):504-521. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2023.501. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2023. PMID: 37749800 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive and conditional gene knockout mice for the study of intervertebral disc degeneration: Current status, decision considerations, and future possibilities.JOR Spine. 2023 Jan 7;6(1):e1242. doi: 10.1002/jsp2.1242. eCollection 2023 Mar. JOR Spine. 2023. PMID: 36994464 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

