The regulatory roles of miR-26a in the development of fracture and osteoblasts
- PMID: 35282137
- PMCID: PMC8848437
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-21-6101
The regulatory roles of miR-26a in the development of fracture and osteoblasts
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a vital role in the bone development and bone regeneration. In this study, we investigated the effects of miR-26a in osteoblasts and fractures.
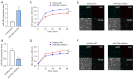
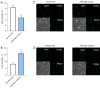
Methods: Human osteoblasts were cultured and used for analysis. To identify differential miRNAs in blood samples from patients with fractures and healthy controls, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis was performed. Human osteoblasts were transfected with miR-26a mimics, miR-26a inhibitor, or their corresponding negative controls (NCs), respectively. MTT assay was performed to identify the effects of miR-26a on the cell viability of osteoblasts. EdU staining was applied to detect the proliferation of osteoblasts. Trypan blue staining was utilized to analyze the effects of miR-26a on the cell death of osteoblasts. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) staining was used to detect apoptotic osteoblasts. Alizarin red S (ARS) staining and qRT-PCR analysis were utilized to measure the mineralized nodule formation to evaluate the bone formation of osteoblasts. Dual luciferase reporter assay and western blot analysis were performed to detect the relationship between miR-26a and its target gene.
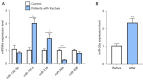
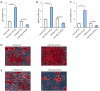
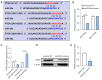
Results: The results of qRT-PCR analysis identified miR-26a as our miRNA of interest and indicated that miR-26a was significantly decreased in patients with fractures. Overexpression of miR-26a significantly increased the cell viability and proliferation of osteoblasts. An increase in miR-26a reduced the cell death and apoptosis of osteoblasts, and promoted the osteoblastic activity and mineralized nodule formation. Dual luciferase reporter assay, qRT-PCR and western blot analysis showed that miR-26a could negatively regulate the expression of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN).
Conclusions: MiR-26a promoted new bone regeneration via regulating the functions of osteoblasts by targeting its target gene PTEN. Therefore, we propose that targeting miR-26a may be a novel therapeutic method for bone regeneration and treating fractures.
Keywords: MicroRNAs (miRNAs); fracture; mineralized nodule formation; osteoblast.
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-21-6101/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-495 Inhibits New Bone Regeneration via Targeting High Mobility Group AT-Hook 2 (HMGA2).Med Sci Monit. 2017 Sep 30;23:4689-4698. doi: 10.12659/msm.904404. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 28963864 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of miR-26a on diabetic rats with myocardial injury by targeting PTEN.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Aug;23(3 Suppl):304-311. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201908_18661. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. Retraction in: Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Oct;24(20):10307. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202010_23363. PMID: 31389595 Retracted.
-
MiRNA-26a Contributes to the Acquisition of Malignant Behaviors of Doctaxel-Resistant Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells through Targeting EZH2.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(2):583-597. doi: 10.1159/000457879. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28214878
-
Osteogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells is modulated by the miR-26a targeting of the SMAD1 transcription factor.J Bone Miner Res. 2008 Feb;23(2):287-95. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.071011. J Bone Miner Res. 2008. PMID: 18197755
-
MicroRNA-185 inhibits the growth and proliferation of osteoblasts in fracture healing by targeting PTH gene through down-regulating Wnt/β -catenin axis: In an animal experiment.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Jun 18;501(1):55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.138. Epub 2018 May 8. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29678580
Cited by
-
HBV Promotes the Proliferation of Liver Cancer Cells through the hsa_circ_0000847/miR-135a Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Sep 15;2022:7332337. doi: 10.1155/2022/7332337. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36159567 Free PMC article.
-
miR-26a is a Key Therapeutic Target with Enormous Potential in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Human Disease.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(18):2550-2570. doi: 10.2174/0109298673271808231116075056. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38204224 Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA H19 contributes to spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury through increasing neuronal pyroptosis by miR-181a-5p/HMGB1 axis.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Jul 5;14(13):5449-5463. doi: 10.18632/aging.204160. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 35793244 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks in the development and treatment of osteoporosis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 5;13:945310. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.945310. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35992137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of circ_000558/miR-1225-5p/ARL4C on Regulating the Proliferation of Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells.J Oncol. 2023 Feb 2;2023:1303748. doi: 10.1155/2023/1303748. eCollection 2023. J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36778920 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
