An overview of the development of EED inhibitors to disable the PRC2 function
- PMID: 35224495
- PMCID: PMC8792826
- DOI: 10.1039/d1md00274k
An overview of the development of EED inhibitors to disable the PRC2 function
Abstract
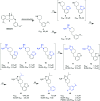
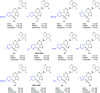
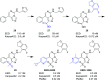
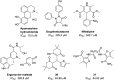
Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) catalyzes the methylation of histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27) and the enrichment of its catalytic product H3K27me3 is responsible for the silencing of tumor suppressor genes and the blocking of transcripts related to immunity and cell terminal differentiation. Aberrations of PRC2 components, such as mutation and overexpression, have been observed in various cancers, which makes PRC2 a potential therapeutic target for cancer. Up to now, targeting the enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2), the catalytic subunit of PRC2, represents the main strategy in the development of PRC2 inhibitors. Although significant progress has been made, new problems also emerge, e.g. the drug resistance caused by secondary mutations. In recent years, more and more efforts have shifted to another new strategy - targeting embryonic ectoderm development (EED) to disrupt its major interactions with other components, which are necessary to the PRC2 function, and some promising results have been obtained. This review summarizes the recent development of EED inhibitors as possible chemotherapy for cancer treatment, which could help accelerate future related research work.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Recent strategies targeting Embryonic Ectoderm Development (EED) for cancer therapy: Allosteric inhibitors, PPI inhibitors, and PROTACs.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Mar 5;231:114144. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114144. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35093670 Review.
-
Wedelolactone disrupts the interaction of EZH2-EED complex and inhibits PRC2-dependent cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 May 30;6(15):13049-59. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3790. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25944687 Free PMC article.
-
EZH2 W113C is a gain-of-function mutation in B-cell lymphoma enabling both PRC2 methyltransferase activation and tazemetostat resistance.J Biol Chem. 2023 Apr;299(4):103073. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.103073. Epub 2023 Feb 27. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 36858198 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of catalytic and non-catalytic activity inhibitors against PRC2-EZH2 complex through multiple high-throughput screening campaigns.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2020 Oct;96(4):1024-1051. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13702. Epub 2020 May 25. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2020. PMID: 32394628
-
Small Molecule Approaches for Targeting the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) in Cancer.J Med Chem. 2020 Dec 24;63(24):15344-15370. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01344. Epub 2020 Dec 7. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 33283516 Review.
Cited by
-
Super-Enhancers, Phase-Separated Condensates, and 3D Genome Organization in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 10;14(12):2866. doi: 10.3390/cancers14122866. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 in Oncology.Cancer Treat Res. 2023;190:273-320. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-45654-1_9. Cancer Treat Res. 2023. PMID: 38113005
-
Long Noncoding RNA XIST Promotes Resistance to Lenvatinib in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via Epigenetic Inhibition of NOD2.J Oncol. 2022 Oct 18;2022:4537343. doi: 10.1155/2022/4537343. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36304988 Free PMC article.
-
Drug resistance mechanism of kinase inhibitors in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 13;14:1097277. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1097277. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36891274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting EED as a key PRC2 complex mediator toward novel epigenetic therapeutics.Drug Discov Today. 2024 Jun;29(6):103986. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2024.103986. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Drug Discov Today. 2024. PMID: 38642703 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

