EBV infection-induced GPX4 promotes chemoresistance and tumor progression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 35105963
- PMCID: PMC9346003
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-022-00939-8
EBV infection-induced GPX4 promotes chemoresistance and tumor progression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
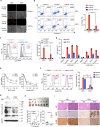
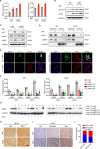
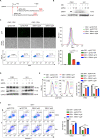
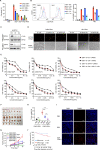
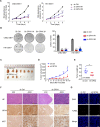
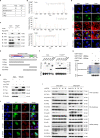
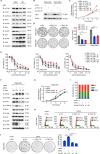
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) was the first oncogenic virus identified in humans. It is primarily associated with multiple lymphoid and epithelial cancers, including nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). However, its association with ferroptosis and its role in cancer therapy resistance have not been fully elucidated. Here, we show that EBV infection reduces the sensitivity of NPC cells to ferroptosis by activating the p62-Keap1-NRF2 signaling pathway in conjunction with upregulation of SLC7A11 and GPX4 expression. Knockdown of endogenous GPX4 or blockade of GPX4 using a specific inhibitor enhanced the chemosensitivity of EBV-infected NPC cells. Functional studies revealed that GPX4 knockdown suppresses the proliferation and colony formation of NPC cells. Mechanistically, GPX4 interacts with the TAK1-TAB1/TAB3 complex, regulates TAK1 kinase activity, and further activates downstream MAPK-JNK and NFκB pathways. High GPX4 expression is correlated with poor clinical outcomes in patients with NPC and other cancer types. Taken together, our findings suggest that EBV infection has important effects on redox homeostasis, revealing a previously unappreciated role for GPX4 in tumor progression. This novel mechanism provides a potential new target for the treatment of EBV-related tumors.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PRMT4 Reduced Erastin-Induced Ferroptosis in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cisplatin-Resistant Cells by Nrf2/GPX4 Pathway.J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2025;44(1):57-71. doi: 10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.2024053754. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39462450
-
EBV-miR-BART8-3p induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through activating NF-κB and Erk1/2 pathways.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Nov 26;37(1):283. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0953-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30477559 Free PMC article.
-
EBV-miR-BART7-3p promotes the EMT and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by suppressing the tumor suppressor PTEN.Oncogene. 2015 Apr 23;34(17):2156-66. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.341. Epub 2014 Oct 27. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25347742
-
Epstein-Barr virus infection and nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 Oct 19;372(1732):20160270. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0270. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28893937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EBV Infection and Glucose Metabolism in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1018:75-90. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-5765-6_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29052133 Review.
Cited by
-
Differences in the landscape of colonized microorganisms in different oral potentially malignant disorders and squamous cell carcinoma: a multi-group comparative study.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Sep 2;24(1):318. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03458-3. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39223464 Free PMC article.
-
ATR-dependent ubiquitin-specific protease 20 phosphorylation confers oxaliplatin and ferroptosis resistance.MedComm (2020). 2023 Dec 20;4(6):e463. doi: 10.1002/mco2.463. eCollection 2023 Dec. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 38124786 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Ferroptosis-Related Prognostic Signature and Subtypes Related to the Immune Microenvironment for Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy.Front Immunol. 2022 May 4;13:895110. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.895110. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35603151 Free PMC article.
-
GSTM3 enhances radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by promoting radiation-induced ferroptosis through USP14/FASN axis and GPX4.Br J Cancer. 2024 Mar;130(5):755-768. doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02574-1. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38228715 Free PMC article.
-
Ancient dormant virus remnant ERVW-1 drives ferroptosis via degradation of GPX4 and SLC3A2 in schizophrenia.Virol Sin. 2024 Feb;39(1):31-43. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2023.09.001. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Virol Sin. 2024. PMID: 37690733 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

