Cabozantinib for HCC Treatment, From Clinical Back to Experimental Models
- PMID: 34722310
- PMCID: PMC8548824
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.756672
Cabozantinib for HCC Treatment, From Clinical Back to Experimental Models
Abstract
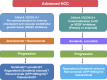
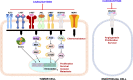
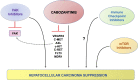
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fourth leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Patients with early-stage HCC can be treated successfully with surgical resection or liver transplantation. However, the usual late diagnosis of HCC precludes curative treatments, and systemic therapies are the only viable option for inoperable patients. Sorafenib, an orally available multikinase inhibitor, is a systemic therapy approved for treating patients with advanced HCC yet providing limited benefits. Consequently, new drugs have been developed to overcome sorafenib resistance and improve patients' prognoses. A new promising strategy is using c-MET inhibitors, such as cabozantinib, as activation of c-MET occurs in up to 40% of HCC patients. In particular, cabozantinib, in combination with the checkpoint inhibitor atezolizumab, is currently in phase 3 clinical trial for HCC, and the results are eagerly awaited. Herein, we summarize and review the drugs approved for the treatment of advanced HCC, mainly focusing on the clinical and preclinical efficacy evaluation of cabozantinib. Also, we report the available preclinical data on cabozantinib-based combination therapies for HCC, current obstacles for cabozantinib therapy, and the future directions for cabozantinib-based treatment for HCC.
Keywords: c-MET; cabozantinib; clinically; combination therapy; hepatocellular carcinoma; multikinase inhibitor; preclinical.
Copyright © 2021 Deng, Solinas and Calvisi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Efficacy of Cabozantinib and Regorafenib for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Adv Ther. 2020 Jun;37(6):2678-2695. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01378-y. Epub 2020 May 18. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 32424805 Free PMC article.
-
Cabozantinib: An evolving therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Treat Rev. 2021 Jul;98:102221. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102221. Epub 2021 May 12. Cancer Treat Rev. 2021. PMID: 34029957 Review.
-
Phase II clinical trial of cabozantinib for the treatment of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation.Future Oncol. 2022 Jun;18(18):2173-2191. doi: 10.2217/fon-2021-1635. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Future Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35287469
-
Pharmacogenetics of the systemic treatment in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Aug 7;25(29):3870-3896. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i29.3870. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31413525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Cabozantinib as a Therapeutic Option for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Landscape and Future Challenges.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2021 Mar 29;8:177-191. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S268310. eCollection 2021. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2021. PMID: 33824862 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LncRNA ERICD interacts with TROAP to regulate TGF-β signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 19;10(14):e34810. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34810. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39148975 Free PMC article.
-
Increased DNA Polymerase Epsilon Catalytic Subunit Expression Predicts Tumor Progression and Modulates Tumor Microenvironment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Cancer. 2022 Jun 3;13(9):2740-2750. doi: 10.7150/jca.64765. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35812186 Free PMC article.
-
miR-26a is a Key Therapeutic Target with Enormous Potential in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Human Disease.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(18):2550-2570. doi: 10.2174/0109298673271808231116075056. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38204224 Review.
-
Cetylpyridinium chloride inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis through regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and apoptosis.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 20;19(9):e0310391. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310391. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39302935 Free PMC article.
-
Protein posttranslational modifications in health and diseases: Functions, regulatory mechanisms, and therapeutic implications.MedComm (2020). 2023 May 2;4(3):e261. doi: 10.1002/mco2.261. eCollection 2023 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37143582 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

