Strategies for genetic manipulation of adult stem cell-derived organoids
- PMID: 34663937
- PMCID: PMC8569115
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-021-00609-8
Strategies for genetic manipulation of adult stem cell-derived organoids
Abstract
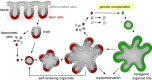
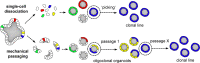
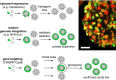
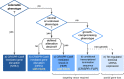
Organoid technology allows the expansion of primary epithelial cells from normal and diseased tissues, providing a unique model for human (patho)biology. In a three-dimensional environment, adult stem cells self-organize and differentiate to gain tissue-specific features. Accessibility to genetic manipulation enables the investigation of the molecular mechanisms underlying cell fate regulation, cell differentiation and cell interactions. In recent years, powerful methodologies using lentiviral transgenesis, CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing, and single-cell readouts have been developed to study gene function and carry out genetic screens in organoids. However, the multicellularity and dynamic nature of stem cell-derived organoids also present challenges for genetic experimentation. In this review, we focus on adult gastrointestinal organoids and summarize the state-of-the-art protocols for successful transgenesis. We provide an outlook on emerging genetic techniques that could further increase the applicability of organoids and enhance the potential of organoid-based techniques to deepen our understanding of gene function in tissue biology.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gene-Edited Fluorescent and Mixed Cerebral Organoids.CRISPR J. 2022 Feb;5(1):53-65. doi: 10.1089/crispr.2021.0070. Epub 2022 Jan 28. CRISPR J. 2022. PMID: 35099270
-
Modeling Wnt signaling by CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing recapitulates neoplasia in human Barrett epithelial organoids.Cancer Lett. 2018 Nov 1;436:109-118. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.08.017. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 30144514 Free PMC article.
-
Human organoids in basic research and clinical applications.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 May 24;7(1):168. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01024-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35610212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment of human fetal hepatocyte organoids and CRISPR-Cas9-based gene knockin and knockout in organoid cultures from human liver.Nat Protoc. 2021 Jan;16(1):182-217. doi: 10.1038/s41596-020-00411-2. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Nat Protoc. 2021. PMID: 33247284
-
Application of CRISPR-Cas9 based gene editing to study the pathogenesis of colon and liver cancer using organoids.Hepatol Int. 2021 Dec;15(6):1309-1317. doi: 10.1007/s12072-021-10237-z. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Hepatol Int. 2021. PMID: 34596864 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Brain In Vitro Model for Pathogen Infection-Related Neurodegeneration Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 13;25(12):6522. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126522. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A knock down strategy for rapid, generic, and versatile modelling of muscular dystrophies in 3D-tissue-engineered-skeletal muscle.Skelet Muscle. 2024 Feb 22;14(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13395-024-00335-5. Skelet Muscle. 2024. PMID: 38389096 Free PMC article.
-
Organoid as a promising tool for primary liver cancer research: a comprehensive review.Cell Biosci. 2024 Aug 27;14(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01287-5. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39192365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocellular-Carcinoma-Derived Organoids: Innovation in Cancer Research.Cells. 2024 Oct 18;13(20):1726. doi: 10.3390/cells13201726. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39451244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STRAIGHT-IN enables high-throughput targeting of large DNA payloads in human pluripotent stem cells.Cell Rep Methods. 2022 Sep 22;2(10):100300. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2022.100300. eCollection 2022 Oct 24. Cell Rep Methods. 2022. PMID: 36313798 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clevers H. Modeling development and disease with organoids. Cell. 2016;165:1586–1597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

