Anticancer effects of melatonin via regulating lncRNA JPX-Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells
- PMID: 34547170
- PMCID: PMC8505851
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16894
Anticancer effects of melatonin via regulating lncRNA JPX-Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells
Abstract
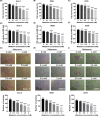
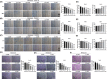
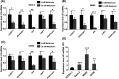
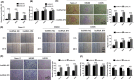
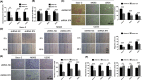
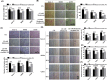
Osteosarcoma (OS) is a type of malignant primary bone cancer, which is highly aggressive and occurs more commonly in children and adolescents. Thus, novel potential drugs and therapeutic methods are urgently needed. In the present study, we aimed to elucidate the effects and mechanism of melatonin on OS cells to provide a potential treatment strategy for OS. The cell survival rate, cell viability, proliferation, migration, invasion and metastasis were examined by trypan blue assay, MTT, colony formation, wound healing, transwell invasion and attachment/detachment assay, respectively. The expression of relevant lncRNAs in OS cells was determined by real-time qPCR analysis. The functional roles of lncRNA JPX in OS cells were further examined by gain and loss of function assays. The protein expression was measured by western blot assay. Melatonin inhibited the cell viability, proliferation, migration, invasion and metastasis of OS cells (Saos-2, MG63 and U2OS) in a dose-dependent manner. Melatonin treatment significantly downregulated the expression of lncRNA JPX in Saos-2, MG63 and U2OS cells. Overexpression of lncRNA JPX into OS cell lines elevated the cell viability and proliferation, which was accompanied by the increased metastasis. We also found that melatonin inhibited the OS progression by suppressing the expression of lncRNA JPX via regulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Our results suggested that melatonin inhibited the biological functions of OS cells by repressing the expression of lncRNA JPX through regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway, which indicated that melatonin might be applied as a potentially useful and effective natural agent in the treatment of OS.
Keywords: LncRNAs; Wnt/β-catenin pathway; melatonin; osteosarcoma; therapeutic methods.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Apigenin inhibits the proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Oncol Rep. 2015 Aug;34(2):1035-41. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4022. Epub 2015 May 29. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26035210
-
LncRNA CRNDE is activated by SP1 and promotes osteosarcoma proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.J Cell Biochem. 2020 Jun;121(5-6):3358-3371. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29607. Epub 2020 Jan 3. J Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31898343
-
LINC01128 regulates the development of osteosarcoma by sponging miR-299-3p to mediate MMP2 expression and activating Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Dec;24(24):14293-14305. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16046. Epub 2020 Oct 27. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33108067 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin cascade in osteosarcoma: The potential of ncRNAs as biomarkers and therapeutics.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Jul;259:155346. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155346. Epub 2024 May 11. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38781762 Review.
-
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Melatonin in Osteosarcoma.Cells. 2019 Dec 12;8(12):1618. doi: 10.3390/cells8121618. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31842295 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Loureirin A Exerts Antikeloid Activity by Antagonizing the TGF-β1/Smad Signalling Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jul 15;2022:8661288. doi: 10.1155/2022/8661288. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9878436. doi: 10.1155/2023/9878436 PMID: 35873644 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Melatonin via MTNR1B regulates METTL3 to protect ileum cell differentiation.Inflammation. 2024 Jul 17. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02098-z. Online ahead of print. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 39014159
-
Melatonin for gastric cancer treatment: where do we stand?Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 17. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03451-7. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39287677 Review.
-
Melatonin acts synergistically with pazopanib against renal cell carcinoma cells through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated mitochondrial and autophagic apoptosis.Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2023 Jul;42(4):487-500. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.22.114. Epub 2023 May 4. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2023. PMID: 37165617 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of melatonin with various signaling pathways: implications for cancer therapy.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Dec 29;22(1):420. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02825-2. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 36581900 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gu Q, Luo Y, Chen C, Jiang D, Huang Q, Wang X. GREM1 overexpression inhibits proliferation, migration and angiogenesis of osteosarcoma. Exp Cell Res. 2019;384:111619. - PubMed
-
- Li L, Wang X, Liu D. MicroRNA‐185 inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion in human osteosarcoma MG63 cells by targeting vesicle‐associated membrane protein 2. Gene. 2019;696:80‐7. - PubMed
-
- Zhang ZF, Xu HH, Hu WH, Hu TY, Wang XB. LINC01116 promotes proliferation, invasion and migration of osteosarcoma cells by silencing p53 and EZH2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:6813‐23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

