Differential roles of GDF15 and FGF21 in systemic metabolic adaptation to the mitochondrial integrated stress response
- PMID: 33718833
- PMCID: PMC7920832
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102181
Differential roles of GDF15 and FGF21 in systemic metabolic adaptation to the mitochondrial integrated stress response
Abstract
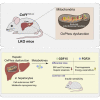
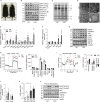
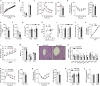
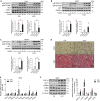
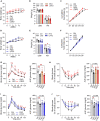
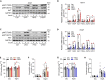
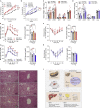
Perturbation of mitochondrial proteostasis provokes cell autonomous and cell non-autonomous responses that contribute to homeostatic adaptation. Here, we demonstrate distinct metabolic effects of hepatic metabokines as cell non-autonomous factors in mice with mitochondrial OxPhos dysfunction. Liver-specific mitochondrial stress induced by a loss-of-function mutation in Crif1 (LKO) leads to aberrant oxidative phosphorylation and promotes the mitochondrial unfolded protein response. LKO mice are highly insulin sensitive and resistant to diet-induced obesity. The hepatocytes of LKO mice secrete large quantities of metabokines, including GDF15 and FGF21, which confer metabolic benefits. We evaluated the metabolic phenotypes of LKO mice with global deficiency of GDF15 or FGF21 and show that GDF15 regulates body and fat mass and prevents diet-induced hepatic steatosis, whereas FGF21 upregulates insulin sensitivity, energy expenditure, and thermogenesis in white adipose tissue. This study reveals that the mitochondrial integrated stress response (ISRmt) in liver mediates metabolic adaptation through hepatic metabokines.
Keywords: Cell Biology; Physiology; Systems Biology.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An adipocyte-specific defect in oxidative phosphorylation increases systemic energy expenditure and protects against diet-induced obesity in mouse models.Diabetologia. 2020 Apr;63(4):837-852. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-05082-7. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Diabetologia. 2020. PMID: 31925461
-
Muscle mitochondrial stress adaptation operates independently of endogenous FGF21 action.Mol Metab. 2015 Nov 24;5(2):79-90. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2015.11.002. eCollection 2016 Feb. Mol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26909316 Free PMC article.
-
ANGPTL6 expression is coupled with mitochondrial OXPHOS function to regulate adipose FGF21.J Endocrinol. 2017 Apr;233(1):105-118. doi: 10.1530/JOE-16-0549. Epub 2017 Feb 9. J Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28184000
-
The roles of FGF21 and GDF15 in mediating the mitochondrial integrated stress response.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 25;14:1264530. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1264530. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37818094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress-induced FGF21 and GDF15 in obesity and obesity resistance.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Nov;32(11):904-915. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2021.08.008. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34526227 Review.
Cited by
-
Beneficial Effects of Low-Grade Mitochondrial Stress on Metabolic Diseases and Aging.Yonsei Med J. 2024 Feb;65(2):55-69. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2023.0131. Yonsei Med J. 2024. PMID: 38288646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inter-tissue communication of mitochondrial stress and metabolic health.Life Metab. 2023 Feb;2(1):load001. doi: 10.1093/lifemeta/load001. Epub 2023 Jan 7. Life Metab. 2023. PMID: 37538245 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Role of GDF15 in Inhibiting Adipogenesis and Hyperlipidemia, Enhancing Cardiovascular Health and Alleviating Inflammation in Metabolic Disorders.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(30):2387-2399. doi: 10.2174/0113816128318741240611114448. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38934286 Review.
-
Mammalian integrated stress responses in stressed organelles and their functions.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Jun;45(6):1095-1114. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01225-0. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38267546 Review.
-
The gastrointestinal tract is a major source of the acute metformin-stimulated rise in GDF15.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 22;14(1):1899. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51866-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38253650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Badman M.K., Pissios P., Kennedy A.R., Koukos G., Flier J.S., Maratos-Flier E. Hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by PPARalpha and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism in ketotic states. Cell Metab. 2007;5:426–437. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

