Early neuroinflammation is associated with lower amyloid and tau levels in cognitively normal older adults
- PMID: 33486003
- PMCID: PMC8793040
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2021.01.010
Early neuroinflammation is associated with lower amyloid and tau levels in cognitively normal older adults
Abstract
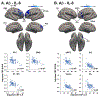
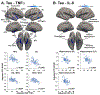
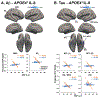
CNS inflammation is a key factor in Alzheimer's Disease (AD), but its relation to pathological Aβ, tau, and APOE4 is poorly understood, particularly prior to the onset of cognitive symptoms. To better characterize early relationships between inflammation, APOE4, and AD pathology, we assessed correlations between cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inflammatory markers and brain levels of Aβ and tau in cognitively normal older adults. Each participant received a lumbar puncture to collect and quantify CSF levels of TNFα, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10, a T1-weighted MRI, and PET scanning with [18F]flortaucipir (FTP; n = 57), which binds to tau tangles and/or [18F]florbetapir (FBP; n = 58), which binds to Aβ. Parallel voxelwise regressions assessed relationships between each CSF inflammatory marker and FTP and FBP SUVR, as well as APOE4*CSF inflammation interactions. Unexpectedly, we detected significant negative associations between regional Aβ and tau PET uptake and CSF inflammatory markers. For Aβ PET, we detected negative associations with CSF IL-6 and IL-8 in regions known to show early accumulation of Aβ (i.e. lateral and medial frontal lobes). For tau PET, negative relationships were observed with CSF TNFα and IL-8, predominantly in regions known to exhibit early tau accumulation (i.e. medial temporal lobe). In subsequent analyses, significant interactions between APOE4 status and IL-8 on Aβ and tau PET levels were observed in spatially distinct regions from those showing CSF-Aβ/tau relationships. Results from the current cross-sectional study support previous findings that neuroinflammation may be protective against AD pathology at a given stage of the disease, and extend these findings to a cognitively normal aging population. This study provides new insight into a dynamic relationship between neuroinflammation and AD pathology and may have implications for whom and when neuroinflammatory therapies may be appropriate.
Keywords: Amyloid-β; Chemokine; Cytokine; Glial activation; Neuroinflammation; PET imaging; Tau.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationships between flortaucipir PET tau binding and amyloid burden, clinical diagnosis, age and cognition.Brain. 2017 Mar 1;140(3):748-763. doi: 10.1093/brain/aww334. Brain. 2017. PMID: 28077397 Free PMC article.
-
Intermediate flortaucipir uptake is associated with Aβ-PET and CSF tau in asymptomatic adults.Neurology. 2020 Mar 17;94(11):e1190-e1200. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008905. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Neurology. 2020. PMID: 32015176
-
Alzheimer's Disease Normative Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers Validated in PET Amyloid-β Characterized Subjects from the Australian Imaging, Biomarkers and Lifestyle (AIBL) study.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;48(1):175-87. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150247. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 26401938
-
Colony Stimulating Factor-1 Receptor: An emerging target for neuroinflammation PET imaging and AD therapy.Bioorg Med Chem. 2024 Feb 15;100:117628. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2024.117628. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Bioorg Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38330850 Review.
-
Insights for Alzheimer's disease pharmacotherapy and current clinical trials.Neurochem Int. 2022 Oct;159:105401. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2022.105401. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Neurochem Int. 2022. PMID: 35842055 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-6 from cerebrospinal fluid causes widespread pain via STAT3-mediated astrocytosis in chronic constriction injury of the infraorbital nerve.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Feb 28;21(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03049-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38419042 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Study of the Pathology and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease and Its Association with Periodontitis.Life (Basel). 2023 Nov 13;13(11):2203. doi: 10.3390/life13112203. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CSF Extracellular Vesicle Aβ42 and Tau/Aβ42 Ratio Are Associated with Cognitive Impairment in Older People with HIV.Viruses. 2023 Dec 31;16(1):72. doi: 10.3390/v16010072. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38257772 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammation, cerebrovascular dysfunction and diurnal cortisol biomarkers in a memory clinic cohort: Findings from the Co-STAR study.Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Sep 9;14(1):364. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-03072-x. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39251589 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease is an inherent, natural part of human brain aging: an integrated perspective.Free Neuropathol. 2022 Jul 8;3:3-17. doi: 10.17879/freeneuropathology-2022-3806. eCollection 2022 Jan. Free Neuropathol. 2022. PMID: 37284149 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander DM, Williams LM, Gatt JM, Dobson-Stone C, Kuan SA, Todd EG, Schofield PR, Cooper NJ, Gordon E, 2007. The contribution of apolipoprotein E alleles on cognitive performance and dynamic neural activity over six decades. Biol. Psychol 75, 229–238. - PubMed
-
- Aloisi F, Carè A, Borsellino G, Gallo P, Rosa S, Bassani A, Cabibbo A, Testa U, Levi G, Peschle C, 1992. Production of hemolymphopoietic cytokines (IL-6, IL-8, colony-stimulating factors) by normal human astrocytes in response to IL-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J. Immunol 149, 2358–2366. - PubMed
-
- Araujo DM, Cotman CW, 1993. Trophic effects of interleukin-4, -7 and -8 on hippocampal neuronal cultures: potential involvement of glial-derived factors. Brain Res. 600, 49–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

