Some ASOs that bind in the coding region of mRNAs and induce RNase H1 cleavage can cause increases in the pre-mRNAs that may blunt total activity
- PMID: 32870273
- PMCID: PMC7515700
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa715
Some ASOs that bind in the coding region of mRNAs and induce RNase H1 cleavage can cause increases in the pre-mRNAs that may blunt total activity
Abstract
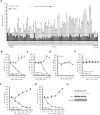
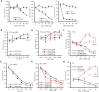
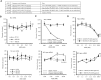
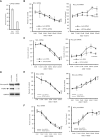
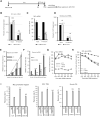
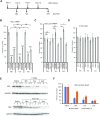
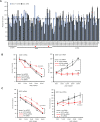
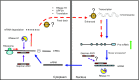
Antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) drugs that trigger RNase H1 cleavage of target RNAs have been developed to treat various diseases. Basic pharmacological principles suggest that the development of tolerance is a common response to pharmacological interventions. In this manuscript, for the first time we report a molecular mechanism of tolerance that occurs with some ASOs. Two observations stimulated our interest: some RNA targets are difficult to reduce with RNase H1 activating ASOs and some ASOs display a shorter duration of activity than the prolonged target reduction typically observed. We found that certain ASOs targeting the coding region of some mRNAs that initially reduce target mRNAs can surprisingly increase the levels of the corresponding pre-mRNAs. The increase in pre-mRNA is delayed and due to enhanced transcription and likely also slower processing. This process requires that the ASOs bind in the coding region and reduce the target mRNA by RNase H1 while the mRNA resides in the ribosomes. The pre-mRNA increase is dependent on UPF3A and independent of the NMD pathway or the XRN1-CNOT pathway. The response is consistent in multiple cell lines and independent of the methods used to introduce ASOs into cells.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Translation can affect the antisense activity of RNase H1-dependent oligonucleotides targeting mRNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 9;46(1):293-313. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1174. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29165591 Free PMC article.
-
RNase H1-Dependent Antisense Oligonucleotides Are Robustly Active in Directing RNA Cleavage in Both the Cytoplasm and the Nucleus.Mol Ther. 2017 Sep 6;25(9):2075-2092. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Mol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28663102 Free PMC article.
-
Antisense oligonucleotides capable of promoting specific target mRNA reduction via competing RNase H1-dependent and independent mechanisms.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 9;9(10):e108625. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108625. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25299183 Free PMC article.
-
Is irrelevant cleavage the price of antisense efficacy?Pharmacol Ther. 2000 Mar;85(3):231-6. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(99)00053-4. Pharmacol Ther. 2000. PMID: 10739877 Review.
-
Antisense oligonucleotide-based therapies for diseases caused by pre-mRNA processing defects.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;825:303-52. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1221-6_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 25201110 Review.
Cited by
-
The Challenges and Strategies of Antisense Oligonucleotide Drug Delivery.Biomedicines. 2021 Apr 16;9(4):433. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9040433. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33923688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA modifications can affect RNase H1-mediated PS-ASO activity.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022 May 11;28:814-828. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.05.024. eCollection 2022 Jun 14. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022. PMID: 35664704 Free PMC article.
-
FSHD Therapeutic Strategies: What Will It Take to Get to Clinic?J Pers Med. 2022 May 25;12(6):865. doi: 10.3390/jpm12060865. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35743650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human disease-causing mutations result in loss of leiomodin 2 through nonsense-mediated mRNA decay.PLoS Genet. 2024 May 15;20(5):e1011279. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011279. eCollection 2024 May. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 38748723 Free PMC article.
-
LNA oligonucleotide mediates an anti-inflammatory effect in autoimmune myocarditis via targeting lactate dehydrogenase B.Immunology. 2022 Feb;165(2):158-170. doi: 10.1111/imm.13421. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Immunology. 2022. PMID: 34606637 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lima W., Wu H., Crooke S.T.. Crooke S.T. Antisense Drug Technology - Principles, Strategies, and Applications. 2008; 2nd ednBoca Raton: CRC Press; 47–74.
-
- Crooke S.T., Vickers T.A., Lima W.F., Wu H.-J.. Crooke S.T. Antisense Drug Technology - Principles, Strategies, and Applications. 2008; 2nd ednBoca Raton: CRC Press; 3–46.
-
- Crooke S.T., Witztum J.L., Bennett C.F., Baker B.F.. RNA-targeted therapeutics. Cell Metab. 2018; 27:714–739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

