Targeting the JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway Using Phytocompounds for Cancer Prevention and Therapy
- PMID: 32545187
- PMCID: PMC7348822
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9061451
Targeting the JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway Using Phytocompounds for Cancer Prevention and Therapy
Abstract
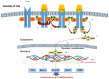
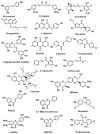
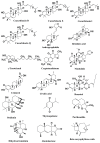
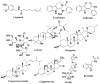
Cancer is a prevalent cause of mortality around the world. Aberrated activation of Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signaling pathway promotes tumorigenesis. Natural agents, including phytochemicals, exhibit potent anticancer activities via various mechanisms. However, the therapeutic potency of phytoconstituents as inhibitors of JAK/STAT signaling against cancer has only come into focus in recent days. The current review highlights phytochemicals that can suppress the JAK/STAT pathway in order to impede cancer cell growth. Various databases, such as PubMed, ScienceDirect, Web of Science, SpringerLink, Scopus, and Google Scholar, were searched using relevant keywords. Once the authors were in agreement regarding the suitability of a study, a full-length form of the relevant article was obtained, and the information was gathered and cited. All the complete articles that were incorporated after the literature collection rejection criteria were applied were perused in-depth and material was extracted based on the importance, relevance, and advancement of the apprehending of the JAK/STAT pathway and their relation to phytochemicals. Based on the critical and comprehensive analysis of literature presented in this review, phytochemicals from diverse plant origins exert therapeutic and cancer preventive effects, at least in part, through regulation of the JAK/STAT pathway. Nevertheless, more preclinical and clinical research is necessary to completely comprehend the capability of modulating JAK/STAT signaling to achieve efficient cancer control and treatment.
Keywords: Janus kinase; cancer; natural compounds; signal transducer and activator of transcription; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phytochemicals Targeting JAK-STAT Pathways in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Insights from Animal Models.Molecules. 2021 May 10;26(9):2824. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092824. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34068714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review: Phytochemicals Targeting JAK/STAT Signaling and IDO Expression in Cancer.Phytother Res. 2015 Jun;29(6):805-17. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5327. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Phytother Res. 2015. PMID: 25787773 Review.
-
Deciphering JAK/STAT signaling pathway: A multifaceted approach to tumorigenesis, progression and therapeutic interventions.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Apr 20;131:111846. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111846. Epub 2024 Mar 23. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38520787 Review.
-
[Research Advances of JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway in Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2019 Jan 20;22(1):45-51. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2019.01.09. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30674393 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Targeting JAK/STAT signaling pathways in treatment of inflammatory bowel disease.Inflamm Res. 2021 Jul;70(7):753-764. doi: 10.1007/s00011-021-01482-x. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34212215 Review.
Cited by
-
Ursolic acid: a natural modulator of signaling networks in different cancers.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Dec 10;22(1):399. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02804-7. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 36496432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p53 Isoforms as Cancer Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 27;14(13):3145. doi: 10.3390/cancers14133145. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35804915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive pan-cancer analysis of STAT3 as a prognostic and immunological biomarker.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 28;13(1):5069. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31226-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36977736 Free PMC article.
-
Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Prevents the Acquisition of a Cancer Stem Cell Phenotype in Ovarian Cancer Tumorspheres through the Inhibition of Src/JAK/STAT3 Signaling.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 23;11(4):1000. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041000. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189618 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Evaluations and Computer-Aided Approaches of Janus Kinases 2 and 3 Inhibitors for Cancer Treatment: A Review.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Sep 4;16(9):1165. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16091165. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39339202 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

