Expression of immune checkpoints and T cell exhaustion markers in early and advanced stages of colorectal cancer
- PMID: 32393998
- PMCID: PMC7511277
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-020-02593-w
Expression of immune checkpoints and T cell exhaustion markers in early and advanced stages of colorectal cancer
Abstract
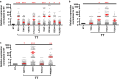
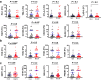
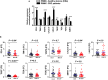
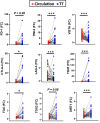
Despite recent advances in colorectal cancer (CRC) treatment, a large proportion of patients show limited responses to therapies, especially in advanced stages. There is an urgent need to identify prognostic biomarkers and/or therapeutic targets in advanced stages, aiming to improve the efficacy of current treatments. We aimed to determine prognostic biomarkers in tumor tissue and circulation of CRC patients, with a special focus on T cell exhaustion markers. We found that mRNA levels of PD-1, TIM-3, CTLA-4, TIGIT, CD160, CD244, KLRG1, TOX2, TOX3, Ki-67, and PRDM1 were elevated in CRC tumor tissues. We also investigated differences in gene expression between early and advanced disease stages. We found that TOX and potentially TIM-3, CTLA-4, VISTA, TIGIT, KLRG1, TOX2, SIRT1, Ki-67, and Helios mRNA levels in tumor tissue were elevated in advanced disease stages, suggesting their potential roles in CRC progression. In contrast, PD-1 and CD160 levels in tumor tissue were downregulated in advanced stages. In the circulation of CRC patients, mRNA levels of PD-1, VISTA and LAG-3 were higher than those of healthy individuals. Moreover, in circulation, PD-1, CTLA-4 and TIGIT mRNA levels were reduced in advanced stages. Interestingly, levels of PD-1 in both tumor tissue and circulation were reduced in advanced stages, suggesting that targeting PD-1 in patients with advanced stages could be less effective. Altogether, these findings suggest some potential T cell exhaustion markers that could be utilized as prognostic biomarkers and/or therapeutic targets for CRC. However, further investigations and validations in larger cohorts are required to confirm these findings.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Immune checkpoints; Prognostic biomarker; T cell exhaustion; Therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune Checkpoints in Circulating and Tumor-Infiltrating CD4+ T Cell Subsets in Colorectal Cancer Patients.Front Immunol. 2019 Dec 17;10:2936. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02936. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31921188 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Colorectal Cancer-Associated Immune Exhaustion Involves T and B Lymphocytes and Conventional NK Cells and Correlates With a Shorter Overall Survival.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 16;12:778329. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.778329. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34975867 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation and repressive histones in the promoters of PD-1, CTLA-4, TIM-3, LAG-3, TIGIT, PD-L1, and galectin-9 genes in human colorectal cancer.Clin Epigenetics. 2018 Aug 6;10(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13148-018-0539-3. Clin Epigenetics. 2018. PMID: 30081950 Free PMC article.
-
Not All Immune Checkpoints Are Created Equal.Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 31;9:1909. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01909. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30233564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel immune checkpoint targets: moving beyond PD-1 and CTLA-4.Mol Cancer. 2019 Nov 6;18(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1091-2. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31690319 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TOX3 Promotes Ovarian Estrogen Synthesis: An RNA-Sequencing and Network Study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Feb 24;11:615846. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.615846. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33716953 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of V-Domain Ig Suppressor of T Cell Activation (VISTA) in Cancer Therapy: Lessons Learned and the Road Ahead.Front Immunol. 2021 May 19;12:676181. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.676181. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34093577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An angiogenesis-associated gene-based signature predicting prognosis and immunotherapy efficacy of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Feb 12;150(2):91. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05606-8. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38347320 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated Forkhead Box (FOX) Genes Association with Survival Prognosis, Anti-tumor Immunity, and Key Targeting Drugs in Colon Adenocarcinoma.Arch Iran Med. 2023 Sep 1;26(9):510-528. doi: 10.34172/aim.2023.77. Arch Iran Med. 2023. PMID: 38310407 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and molecular assessment of an onco-immune signature with prognostic significance in patients with colorectal cancer.Cancer Med. 2022 Mar;11(6):1573-1586. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4568. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 35137551 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

