A Review of SARS-CoV-2 and the Ongoing Clinical Trials
- PMID: 32290293
- PMCID: PMC7177898
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21072657
A Review of SARS-CoV-2 and the Ongoing Clinical Trials
Abstract
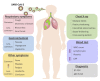
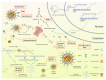
The sudden outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV, later named SARS-CoV-2) in Wuhan, China, which rapidly grew into a global pandemic, marked the third introduction of a virulent coronavirus into the human society, affecting not only the healthcare system, but also the global economy. Although our understanding of coronaviruses has undergone a huge leap after two precedents, the effective approaches to treatment and epidemiological control are still lacking. In this article, we present a succinct overview of the epidemiology, clinical features, and molecular characteristics of SARS-CoV-2. We summarize the current epidemiological and clinical data from the initial Wuhan studies, and emphasize several features of SARS-CoV-2, which differentiate it from SARS-CoV and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), such as high variability of disease presentation. We systematize the current clinical trials that have been rapidly initiated after the outbreak of COVID-19 pandemic. Whereas the trials on SARS-CoV-2 genome-based specific vaccines and therapeutic antibodies are currently being tested, this solution is more long-term, as they require thorough testing of their safety. On the other hand, the repurposing of the existing therapeutic agents previously designed for other virus infections and pathologies happens to be the only practical approach as a rapid response measure to the emergent pandemic, as most of these agents have already been tested for their safety. These agents can be divided into two broad categories, those that can directly target the virus replication cycle, and those based on immunotherapy approaches either aimed to boost innate antiviral immune responses or alleviate damage induced by dysregulated inflammatory responses. The initial clinical studies revealed the promising therapeutic potential of several of such drugs, including favipiravir, a broad-spectrum antiviral drug that interferes with the viral replication, and hydroxychloroquine, the repurposed antimalarial drug that interferes with the virus endosomal entry pathway. We speculate that the current pandemic emergency will be a trigger for more systematic drug repurposing design approaches based on big data analysis.
Keywords: ACE2; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; clinical trials; immunotherapy; pneumonia; replicase; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emergence, Transmission, and Potential Therapeutic Targets for the COVID-19 Pandemic Associated with the SARS-CoV-2.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2020 Aug 25;54(4):767-790. doi: 10.33594/000000254. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32830930
-
Current pharmacological treatments for SARS-COV-2: A narrative review.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 5;882:173328. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173328. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32603692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19: Main therapeutic options.Tunis Med. 2020 Apr;98(4):299-303. Tunis Med. 2020. PMID: 32395792 Review. No abstract available.
-
COVID-19: An overview of the current pharmacological interventions, vaccines, and clinical trials.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Oct;180:114184. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114184. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32739342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 Vaccine: A comprehensive status report.Virus Res. 2020 Oct 15;288:198114. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198114. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32800805 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 host tropism: An in silico analysis of the main cellular factors.Virus Res. 2020 Nov;289:198154. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198154. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32918944 Free PMC article.
-
Methotrexate inhibits SARS-CoV-2 virus replication "in vitro".J Med Virol. 2021 Mar;93(3):1780-1785. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26512. Epub 2020 Sep 28. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 32926453 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral potential of diminazene aceturate against SARS-CoV-2 proteases using computational and in vitro approaches.Chem Biol Interact. 2022 Nov 1;367:110161. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110161. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Chem Biol Interact. 2022. PMID: 36116513 Free PMC article.
-
Furin Inhibitors Block SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Cleavage to Suppress Virus Production and Cytopathic Effects.Cell Rep. 2020 Oct 13;33(2):108254. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108254. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 33007239 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemic Stroke among the Symptoms Caused by the COVID-19 Infection.J Clin Med. 2020 Aug 19;9(9):2688. doi: 10.3390/jcm9092688. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32825182 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen N., Zhou M., Dong X., Qu J., Gong F., Han Y., Qiu Y., Wang J., Liu Y., Wei Y., et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet. 2020;395:507–513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan J.F.-W., Yuan S., Kok K.-H., To K.K.-W., Chu H., Yang J., Xing F., Liu J., Yip C.C.-Y., Poon R.W.-S., et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: A study of a family cluster. Lancet. 2020;395:514–523. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous