miR-26a-5p Inhibit Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion Through Mediated Wnt5a
- PMID: 32273724
- PMCID: PMC7108881
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S241199
miR-26a-5p Inhibit Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion Through Mediated Wnt5a
Abstract
Purpose: Gastric cancer (GC) is a malignant disease of digestive tract. Clinically, radiation therapy is widely applied in treating GC, while with undesirable outcome due to tumor re-proliferation and recurrence and metastasis after radiation. Therefore, it is crucial to explore potential molecular mechanisms to develop therapeutic strategies. The present study found that miR-26a-5p has low expression in GC patients and could regulate Wnt5a to inhibit tumor growth, which was a potential therapeutic target for GC. To explore the expression and related mechanism of miR-26a-5p and Wnt5a in GC.
Patients and methods: MiR-26a-5p and Wnt5a were extracted from the transcriptome data of GC downloaded from TCGA database for analysis. The expression levels of miR-26a-5p and Wnt5a in patients' tissues and serum were detected by qRT-PCR, and their correlation with patients' pathological data and survival was analyzed. In addition, miR-26a-5p and Wnt5a overexpression and inhibition vectors were transfected into cells to observe the effects on the proliferation, invasion and apoptosis of GC cells. The relationship between miR-26a-5p and Wnt5a was analyzed by dual luciferase report.
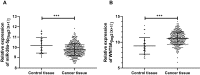
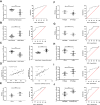
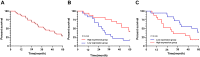
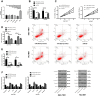
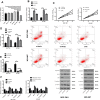
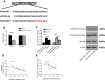
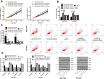
Results: The database and clinical samples showed that miR-26a-5p level was low while Wnt5a was high in GC. MiR-26a-5p level decreased in patients with stage III+IV, lymphatic metastasis and tumor ≥3cm, and Wnt5a was contrary to that of the miR-26a-5p, with diagnostic value. Overexpressed miR-26a-5p and inhibited Wnt5a enhanced apoptosis, decreased proliferation and invasion, reduced Bcl-2 and β-catenin proteins, and elevated Caspase 3, E-cadherin and Bax proteins, while inhibited miR-26a-5p and over-expressed Wnt5a showed the opposite results. Dual luciferase report confirmed that miR-26a-5p targeted to regulate Wnt5a, and rescue experiments found that these effects could be counteracted by reducing miR-26a-5p level.
Conclusion: Overexpressed miR-26a-5p can inhibit Wnt5a expression, promote cell apoptosis, and suppress cell proliferation and invasion in GC.
Keywords: TCGA; Wnt5a; diagnosis; gastric cancer; miR-26a-5p; survival.
© 2020 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Yu Li and Peng Wang contributed equally to this study as co-first authors. The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-26a-5p inhibits proliferation, invasion and metastasis by repressing the expression of Wnt5a in papillary thyroid carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Aug 16;12:6605-6616. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S205994. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31496749 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of miR-26a-5p/Wnt5a signaling in gambogic acid-induced inhibition of gastric cancer.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021 Apr;35(4):e22721. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22721. Epub 2021 Feb 3. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33533530
-
MiR-26a-5p Targets WNT5A to Protect Cardiomyocytes from Injury Due to Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Through the Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway.Int Heart J. 2021 Sep 30;62(5):1145-1152. doi: 10.1536/ihj.21-054. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Int Heart J. 2021. PMID: 34544974
-
[MicroRNA-26a-5p targets Wnt5a to regulate osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cell from inflammatory microenvironment].Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Oct 9;54(10):662-669. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2019.10.003. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31607001 Chinese.
-
LncRNA HCP5 Induces Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation, Invasion, and EMT Processes Through the miR-186-5p/WNT5A Axis Under Hypoxia.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 11;9:663654. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.663654. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34178988 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Learning from Embryogenesis-A Comparative Expression Analysis in Melanoblast Differentiation and Tumorigenesis Reveals miRNAs Driving Melanoma Development.J Clin Med. 2021 May 24;10(11):2259. doi: 10.3390/jcm10112259. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34073664 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-26a inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by targeting FAM98A in breast cancer.Oncol Lett. 2021 May;21(5):367. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12628. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33747224 Free PMC article.
-
Up-Regulation of miR-26a-5p Inhibits E2F7 to Regulate the Progression of Renal Carcinoma Cells.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Nov 17;12:11723-11733. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S271710. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 33235501 Free PMC article.
-
BRD4 expression and its regulatory interaction with miR-26a-3p, DLG5-AS1, and JMJD1C-AS1 lncRNAs in gastric cancer progression.Discov Oncol. 2024 Aug 16;15(1):356. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01230-7. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39152304 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of Long Noncoding RNA LINC00240 Inhibits Esophageal Cancer Progression by Regulating miR-26a-5p.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Oct 5;2022:1071627. doi: 10.1155/2022/1071627. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36262998 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

