Primary Alcohol-Activated Human and Mouse Hepatic Stellate Cells Share Similarities in Gene-Expression Profiles
- PMID: 32258954
- PMCID: PMC7109347
- DOI: 10.1002/hep4.1483
Primary Alcohol-Activated Human and Mouse Hepatic Stellate Cells Share Similarities in Gene-Expression Profiles
Abstract
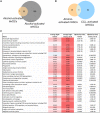
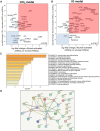
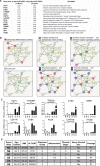
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is a leading cause of cirrhosis in the United States, which is characterized by extensive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins and formation of a fibrous scar. Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are the major source of collagen type 1 producing myofibroblasts in ALD fibrosis. However, the mechanism of alcohol-induced activation of human and mouse HSCs is not fully understood. We compared the gene-expression profiles of primary cultured human HSCs (hHSCs) isolated from patients with ALD (n = 3) or without underlying liver disease (n = 4) using RNA-sequencing analysis. Furthermore, the gene-expression profile of ALD hHSCs was compared with that of alcohol-activated mHSCs (isolated from intragastric alcohol-fed mice) or CCl4-activated mouse HSCs (mHSCs). Comparative transcriptome analysis revealed that ALD hHSCs, in addition to alcohol-activated and CCl4-activated mHSCs, share the expression of common HSC activation (Col1a1 [collagen type I alpha 1 chain], Acta1 [actin alpha 1, skeletal muscle], PAI1 [plasminogen activator inhibitor-1], TIMP1 [tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1], and LOXL2 [lysyl oxidase homolog 2]), indicating that a common mechanism underlies the activation of human and mouse HSCs. Furthermore, alcohol-activated mHSCs most closely recapitulate the gene-expression profile of ALD hHSCs. We identified the genes that are similarly and uniquely up-regulated in primary cultured alcohol-activated hHSCs and freshly isolated mHSCs, which include CSF1R (macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor), PLEK (pleckstrin), LAPTM5 (lysosmal-associated transmembrane protein 5), CD74 (class I transactivator, the invariant chain), CD53, MMP9 (matrix metallopeptidase 9), CD14, CTSS (cathepsin S), TYROBP (TYRO protein tyrosine kinase-binding protein), and ITGB2 (integrin beta-2), and other genes (compared with CCl4-activated mHSCs). Conclusion: We identified genes in alcohol-activated mHSCs from intragastric alcohol-fed mice that are largely consistent with the gene-expression profile of primary cultured hHSCs from patients with ALD. These genes are unique to alcohol-induced HSC activation in two species, and therefore may become targets or readout for antifibrotic therapy in experimental models of ALD.
© 2020 The Authors. Hepatology Communications published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc., on behalf of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
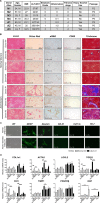
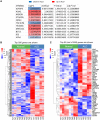
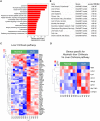
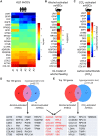
Similar articles
-
Coordinated signaling of activating transcription factor 6α and inositol-requiring enzyme 1α regulates hepatic stellate cell-mediated fibrogenesis in mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021 May 1;320(5):G864-G879. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00453.2020. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33728997 Free PMC article.
-
Igf2bp2 knockdown improves CCl4-induced liver fibrosis and TGF-β-activated mouse hepatic stellate cells by regulating Tgfbr1.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Sep;110:108987. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108987. Epub 2022 Jul 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35820364
-
P300 Acetyltransferase Mediates Stiffness-Induced Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells Into Tumor-Promoting Myofibroblasts.Gastroenterology. 2018 Jun;154(8):2209-2221.e14. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.02.015. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Gastroenterology. 2018. PMID: 29454793 Free PMC article.
-
The miR-139-5p/peripheral myelin protein 22 axis modulates TGF-β-induced hepatic stellate cell activation and CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in mice.Life Sci. 2021 Jul 1;276:119294. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119294. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33675896
-
Gas6/Axl pathway is activated in chronic liver disease and its targeting reduces fibrosis via hepatic stellate cell inactivation.J Hepatol. 2015 Sep;63(3):670-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.04.013. Epub 2015 Apr 20. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25908269 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Generation of functionally competent hepatic stellate cells from human stem cells to model liver fibrosis in vitro.Stem Cell Reports. 2022 Nov 8;17(11):2531-2547. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2022.09.010. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Stem Cell Reports. 2022. PMID: 36270282 Free PMC article.
-
Development of human iPSC-derived quiescent hepatic stellate cell-like cells for drug discovery and in vitro disease modeling.Stem Cell Reports. 2021 Dec 14;16(12):3050-3063. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.11.002. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Stem Cell Reports. 2021. PMID: 34861166 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics of Human Fibrotic Diseases: Disordered Wound Healing Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 14;21(22):8590. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228590. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33202590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Down-Regulation of CXXC5 De-Represses MYCL1 to Promote Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 21;9:680344. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.680344. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34621736 Free PMC article.
-
Nondegradable Collagen Increases Liver Fibrosis but Not Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Mice.Am J Pathol. 2021 Sep;191(9):1564-1579. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2021.05.019. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Am J Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34119473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shang L, Hosseini M, Liu X, Kisseleva T, Brenner DA. Human hepatic stellate cell isolation and characterization. J Gastroenterol 2018;53:6‐17. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

