The miR-26a/AP-2α/Nanog signaling axis mediates stem cell self-renewal and temozolomide resistance in glioma
- PMID: 31534499
- PMCID: PMC6735392
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.33800
The miR-26a/AP-2α/Nanog signaling axis mediates stem cell self-renewal and temozolomide resistance in glioma
Abstract
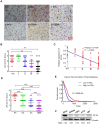
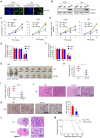
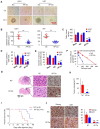
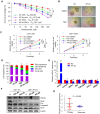
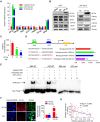
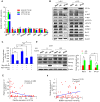
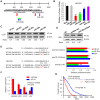
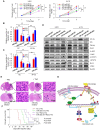
Aberrant expression of transcription factor AP-2α has been functionally associated with various cancers, but its clinical significance and molecular mechanisms in human glioma are largely elusive. Methods: AP-2α expression was analyzed in human glioma tissues by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and in glioma cell lines by Western blot. The effects of AP-2α on glioma cell proliferation, migration, invasion and tumor formation were evaluated by the 3-(4,5-dimethyNCthiazol-2-yl)-25-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) and transwell assays in vitro and in nude mouse models in vivo. The influence of AP-2α on glioma cell stemness was analyzed by sphere-formation, self-renewal and limiting dilution assays in vitro and in intracranial mouse models in vivo. The effects of AP-2α on temozolomide (TMZ) resistance were detected by the MTT assay, cell apoptosis, real-time PCR analysis, western blotting and mouse experiments. The correlation between AP-2α expression and the expression of miR-26a, Nanog was determined by luciferase reporter assays, electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) and expression analysis. Results: AP-2α expression was downregulated in 58.5% of glioma tissues and in 4 glioma cell lines. AP-2α overexpression not only reduced the proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma cell lines but also suppressed the sphere-formation and self-renewal abilities of glioma stem cells in vitro. Moreover, AP-2α overexpression inhibited subcutaneous and intracranial xenograft tumor growth in vivo. Furthermore, AP-2α enhanced the sensitivity of glioma cells to TMZ. Finally, AP-2α directly bound to the regulatory region of the Nanog gene, reduced Nanog, Sox2 and CD133 expression. Meanwhile, AP-2α indirectly downregulated Nanog expression by inhibiting the interleukin 6/janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (IL6/JAK2/STAT3) signaling pathway, consequently decreasing O6-methylguanine methyltransferase (MGMT) and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression. In addition, miR-26a decreased AP-2α expression by binding to the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of AP-2α and reversed the tumor suppressive role of AP-2α in glioma, which was rescued by a miR-26a inhibitor. TMZ and the miR-26a inhibitor synergistically suppressed intracranial GSC growth. Conclusion: These results suggest that AP-2α reduces the stemness and TMZ resistance of glioma by inhibiting the Nanog/Sox2/CD133 axis and IL6/STAT3 signaling pathways. Therefore, AP-2α and miR-26a inhibition might represent a new target for developing new therapeutic strategies in TMZ resistance and recurrent glioma patients.
Keywords: AP-2α; Nanog; STAT3; TMZ resistance; glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs); glioma; miR-26a.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AP-2α decreases TMZ resistance of recurrent GBM by downregulating MGMT expression and improving DNA damage.Life Sci. 2024 Nov 15;357:123111. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.123111. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39369843
-
Warburg effect-promoted exosomal circ_0072083 releasing up-regulates NANGO expression through multiple pathways and enhances temozolomide resistance in glioma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 May 11;40(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01942-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33975615 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-29b promotes cell sensitivity to Temozolomide by targeting STAT3 in glioma.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Feb;24(4):1922-1931. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202002_20370. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32141561
-
Integrative analysis of cell adhesion molecules in glioblastoma identified prostaglandin F2 receptor inhibitor (PTGFRN) as an essential gene.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jun 11;22(1):642. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09682-2. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35690717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The oncogenic potential of NANOG: An important cancer induction mediator.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Apr;236(4):2443-2458. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30063. Epub 2020 Sep 22. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 32960465 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of RNA modification in the generation of acquired drug resistance in glioma.Front Genet. 2022 Nov 11;13:1032286. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1032286. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36437944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Value of miR-296 and miR-517c in Evaluating the Prognosis of Patients with Glioma after Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy.J Oncol. 2021 Dec 16;2021:6082458. doi: 10.1155/2021/6082458. eCollection 2021. J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34956365 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis based on vesicle trafficking-related genes identifying CNIH4 as a novel therapeutic target for glioma.Cancer Med. 2023 Jun;12(11):12943-12959. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5947. Epub 2023 Apr 16. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37062068 Free PMC article.
-
Glioma Stem Cells as Promoter of Glioma Progression: A Systematic Review of Molecular Pathways and Targeted Therapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 22;25(14):7979. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147979. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of Autophagy Regulation in Glioblastoma with Temozolomide Resistance.Cells. 2024 Aug 11;13(16):1332. doi: 10.3390/cells13161332. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39195222 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jue TR, Mcdonald KL. The challenges associated with molecular targeted therapies for glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 2016;127:427–434. - PubMed
-
- McNamara MG, Lwin Z, Jiang H, Chung C, Millar BA, Sahgal A. et al. Conditional probability of survival and post-progression survival in patients with glioblastoma in the temozolomide treatment era. J Neurooncol. 2014;117:153–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

