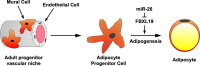
miR-26 suppresses adipocyte progenitor differentiation and fat production by targeting Fbxl19
- PMID: 31488578
- PMCID: PMC6771383
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.328955.119
miR-26 suppresses adipocyte progenitor differentiation and fat production by targeting Fbxl19
Abstract
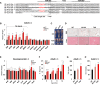
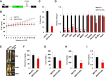
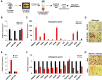
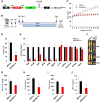
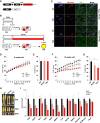
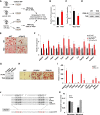
Fat storage in adult mammals is a highly regulated process that involves the mobilization of adipocyte progenitor cells (APCs) that differentiate to produce new adipocytes. Here we report a role for the broadly conserved miR-26 family of microRNAs (miR-26a-1, miR-26a-2, and miR-26b) as major regulators of APC differentiation and adipose tissue mass. Deletion of all miR-26-encoding loci in mice resulted in a dramatic expansion of adipose tissue in adult animals fed normal chow. Conversely, transgenic overexpression of miR-26a protected mice from high-fat diet-induced obesity. These effects were attributable to a cell-autonomous function of miR-26 as a potent inhibitor of APC differentiation. miR-26 blocks adipogenesis, at least in part, by repressing expression of Fbxl19, a conserved miR-26 target without a previously known role in adipocyte biology that encodes a component of SCF-type E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes. These findings have therefore revealed a novel pathway that plays a critical role in regulating adipose tissue formation in vivo and suggest new potential therapeutic targets for obesity and related disorders.
Keywords: Fbxl19; adipocyte progenitor cell; adipogenesis; miR-26; microRNA; obesity; white adipose tissue.
© 2019 Acharya et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AP2-microRNA-26a overexpression reduces visceral fat mass and blood lipids.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021 May 15;528:111217. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2021.111217. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 33667597
-
MiR-27 orchestrates the transcriptional regulation of brown adipogenesis.Metabolism. 2014 Feb;63(2):272-82. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.10.004. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Metabolism. 2014. PMID: 24238035
-
miR-199a-3p regulates brown adipocyte differentiation through mTOR signaling pathway.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018 Nov 15;476:155-164. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2018.05.005. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29753771
-
microRNAs in the regulation of adipogenesis and obesity.Curr Mol Med. 2011 Jun;11(4):304-16. doi: 10.2174/156652411795677990. Curr Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21506921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipogenic miRNA and meta-signature miRNAs involved in human adipocyte differentiation and obesity.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 28;7(26):40830-40845. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8518. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27049726 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-190 promotes malignant transformation and progression of human urothelial cells through CDKN1B/p27 inhibition.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Apr 29;21(1):241. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01937-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33926470 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic β cell microRNA-26a alleviates type 2 diabetes by improving peripheral insulin sensitivity and preserving β cell function.PLoS Biol. 2020 Feb 24;18(2):e3000603. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000603. eCollection 2020 Feb. PLoS Biol. 2020. PMID: 32092075 Free PMC article.
-
Association of DNA methylation signatures with premature ageing and cardiovascular death in patients with end-stage kidney disease: a pilot epigenome-wide association study.Epigenetics. 2023 Dec;18(1):2214394. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2023.2214394. Epigenetics. 2023. PMID: 37207321 Free PMC article.
-
miR-26a is a Key Therapeutic Target with Enormous Potential in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Human Disease.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(18):2550-2570. doi: 10.2174/0109298673271808231116075056. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38204224 Review.
-
A Review of miRNAs as Biomarkers and Effect of Dietary Modulation in Obesity Associated Cognitive Decline and Neurodegenerative Disorders.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Oct 7;14:756499. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.756499. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34690698 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
