Necrostatin-1 Attenuates Renal Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury via Meditation of HIF-1α/mir-26a/TRPC6/PARP1 Signaling
- PMID: 31422287
- PMCID: PMC6706591
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.06.025
Necrostatin-1 Attenuates Renal Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury via Meditation of HIF-1α/mir-26a/TRPC6/PARP1 Signaling
Abstract
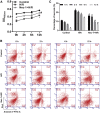
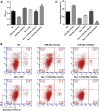
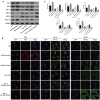
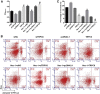
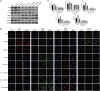
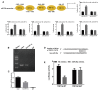
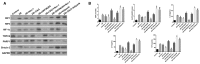
Necroptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation are major contributors to the pathogenesis of ischemic acute kidney injury. Necrostatin-1 (Nec-1), an inhibitor of the kinase domain of receptor-interacting protein kinase-1 (RIP1), has been reported to regulate renal ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) injury; however, its underlying mechanism of action remains unclear. HK-2 cells were used to create an in vitro I/R model, in which the cells were subjected to hypoxia, followed by 2, 6, and 12 h of reoxygenation. For the in vivo study, a rat model of renal I/R was established in which samples of rat blood serum and kidney tissue were harvested after reperfusion to assess renal function and detect histological changes. Cell viability and necroptosis were analyzed using the Cell Counting Kit (CCK)-8 assay and flow cytometry, respectively. The expression levels of molecules associated with necroptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation were determined by real-time PCR, western blotting, immunofluorescence staining, and ELISA. Luciferase and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays were performed to confirm the relevant downstream signaling pathway. We found that pretreatment with Nec-1 significantly decreased hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and miR-26a expression, as well as the levels of factors associated with necroptosis (RIP1, RIP3, and Sirtuin-2), oxidative stress (malondialdehyde [MDA], NADP+/NADPH ratio), and inflammation (interleukin [IL]-1β, IL-10, and tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α]) in I/R injury cells and the rat model. However, these effects could be reversed by miR-26a overexpression or TRPC6 knockdown. Mechanistic studies demonstrated that HIF-1α directly binds to the promoter region of miR-26a, and that TRPC6 is a potential target gene for miR-26a. Our findings indicate that Nec-1 can effectively protect against renal I/R injury by inhibiting necroptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation, and may exert its effects through mediation of the HIF-1α/miR-26a/TRPC6/PARP1 signaling pathway.
Keywords: HIF-1α; Nec-1; TRPC6; inflammation; ischemic/reperfusion injury; miR-26a; necroptosis; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
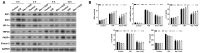
Similar articles
-
Ischemic preconditioning-induced protective effect for promoting angiogenesis in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating miR-376c-3p/HIF-1α/VEGF axis in male rats.Life Sci. 2022 Jun 15;299:120357. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120357. Epub 2022 Jan 29. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35092734
-
Renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury is promoted by transcription factor NF-kB p65, which inhibits TRPC6 expression by activating miR-150.Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2024;86(3):369-382. doi: 10.3233/CH-231979. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2024. PMID: 37980653 Free PMC article.
-
Rip 1-dependent endothelial necroptosis participates in ischemia-reperfusion injury of mouse flap.J Dermatol Sci. 2020 Jan;97(1):30-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2019.11.009. Epub 2019 Nov 28. J Dermatol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31831282
-
miR-21 contributes to renal protection by targeting prolyl hydroxylase domain protein 2 in delayed ischaemic preconditioning.Nephrology (Carlton). 2017 May;22(5):366-373. doi: 10.1111/nep.12787. Nephrology (Carlton). 2017. PMID: 27030384
-
Effects of PGC1α on myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury and the underlying mechanisms.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020 Oct 28;45(10):1155-1163. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2020.190215. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020. PMID: 33268575 Chinese, English.
Cited by
-
How to Best Protect Kidneys for Transplantation-Mechanistic Target.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 23;12(5):1787. doi: 10.3390/jcm12051787. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36902572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Hypothermic Machine Perfusion to Ameliorate Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Donor Organs.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 29;13:848352. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.848352. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35572574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathway from Acute Kidney Injury to Chronic Kidney Disease: Molecules Involved in Renal Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 13;24(18):14019. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814019. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorofenidone Alleviates Renal Fibrosis by Inhibiting Necroptosis Through RIPK3/MLKL Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Dec 16;11:534775. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.534775. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33390935 Free PMC article.
-
Minimizing Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Xenotransplantation.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 9;12:681504. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.681504. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34566955 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Toronyi E. [Role of apoptosis in the kidney after reperfusion] Orv. Hetil. 2008;149:305–315. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

