Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 3-(quinolin-4-ylamino)benzenesulfonamidesAQ3 as carbonic anhydrase isoforms I and II inhibitors
- PMID: 31411080
- PMCID: PMC6713088
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2019.1652282
Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 3-(quinolin-4-ylamino)benzenesulfonamidesAQ3 as carbonic anhydrase isoforms I and II inhibitors
Abstract
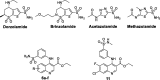
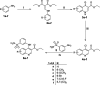
Carbonic anhydrases (CAs, EC 4.2.1.1) are crucial metalloenzymes that are involved in diverse bioprocesses. We report the synthesis and biological evaluation of novel series of benzenesulfonamides incorporating un/substituted ethyl quinoline-3-carboxylate moieties. The newly synthesised compounds were in vitro evaluated as inhibitors of the cytosolic human (h) isoforms hCA I and II. Both isoforms hCA I and II were inhibited by the quinolines reported here in variable degrees: hCA I was inhibited with KIs in the range of 0.966-9.091 μM, whereas hCA II in the range of 0.083-3.594 μM. The primary 7-chloro-6-flouro substituted sulphfonamide derivative 6e (KI = 0.083 μM) proved to be the most active quinoline in inhibiting hCA II, whereas, its secondary sulfonamide analog failed to inhibit the hCA II up to 10 μM, confirming the crucial role of the primary sulphfonamide group, as a zinc-binding group for CA inhibitory activity.
Keywords: carbonic anhydrase; cytosolic isoforms hCA I and II; quinolines; synthesis.
Figures
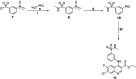
Similar articles
-
Synthesis and evaluation of sulfonamide-bearing thiazole as carbonic anhydrase isoforms hCA I and hCA II.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016 Dec;31(6):1300-5. doi: 10.3109/14756366.2015.1128426. Epub 2016 Jan 8. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26744900
-
Novel indolin-2-one-based sulfonamides as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Synthesis, in vitro biological evaluation against carbonic anhydrases isoforms I, II, IV and VII and molecular docking studies.Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Feb 15;127:521-530. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.01.017. Epub 2017 Jan 11. Eur J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28109946
-
Synthesis and carbonic anhydrase inhibitory activities of new thienyl-substituted pyrazoline benzenesulfonamides.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016;31(sup2):1-5. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2016.1181627. Epub 2016 Jul 19. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27435177
-
Structure-activity relationship of human carbonic anhydrase-II inhibitors: Detailed insight for future development as anti-glaucoma agents.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Jan;95:103557. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103557. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 31911296 Review.
-
The Effect of Nanoparticles on the Structure and Enzymatic Activity of Human Carbonic Anhydrase I and II.Molecules. 2020 Sep 25;25(19):4405. doi: 10.3390/molecules25194405. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32992797 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel benzofuran-based sulphonamides as selective carbonic anhydrases IX and XII inhibitors: synthesis and in vitro biological evaluation.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020 Dec;35(1):298-305. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2019.1697250. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31809607 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Novel Quinoline-Based Sulfonamides as Selective Cancer-Associated Carbonic Anhydrase Isoform IX Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 15;22(20):11119. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011119. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681794 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and molecular docking of new fused 1H-pyrroles, pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidines and pyrrolo[3,2-e][1, 4]diazepine derivatives as potent EGFR/CDK2 inhibitors.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):1884-1902. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2096019. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35801486 Free PMC article.
-
Uracil as a Zn-Binding Bioisostere of the Allergic Benzenesulfonamide in the Design of Quinoline-Uracil Hybrids as Anticancer Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Apr 19;15(5):494. doi: 10.3390/ph15050494. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631321 Free PMC article.
-
Topo II inhibition and DNA intercalation by new phthalazine-based derivatives as potent anticancer agents: design, synthesis, anti-proliferative, docking, and in vivo studies.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):299-314. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2021.2007905. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34894955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- (a) Supuran CT. Carbonic anhydrases: novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2008;7:168–81., - PubMed
- (b) Alterio V, Di Fiore A, D’Ambrosio K, et al. . Multiple binding modes of inhibitors to carbonic anhydrases: how to design specific drugs targeting 15 different isoforms? Chem Rev 2012;112:4421–68., - PubMed
- (c) Supuran CT. Applications of carbonic anhydrases inhibitors in renal and central nervous system diseases. Expert Opin Ther Pat 2018;28:713–21., - PubMed
- (d) Supuran CT. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and their potential in a range of therapeutic areas. Expert Opin Ther Pat 2018;28:709–12., - PubMed
- (e) Supuran CT. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors as emerging agents for the treatment and imaging of hypoxic tumors. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2018;27:963–70., - PubMed
- (f) Nocentini A, Supuran CT. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors as antitumor/antimetastatic agents: a patent review (2008-2018). Expert Opin Ther Pat 2018;28:729–40. - PubMed
-
- (a) Supuran CT. Structure-based drug discovery of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2012;27:759–72., - PubMed
- (b) De Simone G, Supuran CT. (In)organic anions as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. J Inorg Biochem 2012;111:117–29., - PubMed
- (c) Supuran CT. Carbonic anhydrase inhibition and the management of hypoxic tumors. Metabolites 2017;7:E48, - PMC - PubMed
- (d) Supuran CT. Carbonic anhydrases and metabolism. Metabolites 2018;8:E25., - PMC - PubMed
- (e) Supuran CT. Carbon- versus sulphur-based zinc binding groups for carbonic anhydrase inhibitors? J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2018;33:485–95. - PMC - PubMed
-
- (a) Supuran CT. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2010;20:3467–74., - PubMed
- (b) Briganti F, Pierattelli R, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Part 37. Novel classes of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and their interaction with the native and cobalt-substituted enzyme: kinetic and spectroscopic investigations. Eur J Med Chem 1996;31:1001–10.,
- (c) Supuran CT. How many carbonic anhydrase inhibition mechanisms exist? J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2016;31:345–60., - PubMed
- (d) Supuran CT. Advances in structure-based drug discovery of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Expert Opin Drug Discov 2017;12:61–88., - PubMed
- (e) Supuran CT. Structure and function of carbonic anhydrases. Biochem J 2016;473:2023–32., - PubMed
- (f) Neri D, Supuran CT. Interfering with pH regulation in tumours as a therapeutic strategy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2011;10:767–77., - PubMed
- (g) Supuran CT, Vullo D, Manole G, et al. . Designing of novel carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and activators. Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents 2004;2:49–68. - PubMed
-
- (a) Pastorekova S, Parkkila S, Pastorek J, Supuran CT. Carbonic anhydrases: current state of the art, therapeutic applications and future prospects. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2004;19:199–229., - PubMed
- (b) Supuran CT, Capasso C. The eta-class carbonic anhydrases as drug targets for antimalarial agents. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2015;19:551–63., - PubMed
- (c) Capasso C, Supuran CT. Bacterial, fungal and protozoan carbonic anhydrases as drug targets. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2015;19:1689–704., - PubMed
- (d) Supuran CT, Capasso C. Biomedical applications of prokaryotic carbonic anhydrases. Expert Opin Ther Pat 2018;28:745–54., - PubMed
- (e) Supuran CT, Capasso C. An overview of the bacterial carbonic anhydrases. Metabolites 2017;7:56. - PMC - PubMed
-
- (a) Supuran CT. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and activators for novel therapeutic applications. Future Med Chem 2011;3:1165–80., - PubMed
- (b) Akocak S, Lolak N, Bua S, et al. . Discovery of novel 1,3-diaryltriazene sulfonamides as carbonic anhydrase I, II, VII, and IX inhibitors. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2018;33:1575–80., - PMC - PubMed
- (c) Winum JY, Temperini C, El Cheikh K, et al. . Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: clash with Ala65 as a means for designing inhibitors with low affinity for the ubiquitous isozyme II, exemplified by the crystal structure of the topiramate sulfamide analogue. J Med Chem 2006;49:7024–31., - PubMed
- (d) Supuran CT. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors in the treatment and prophylaxis of obesity. Expert Opin Ther Pat 2003;13:1545–50.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
