Ethnobotanical Knowledge in Sete Cidades, Azores Archipelago: First Ethnomedicinal Report
- PMID: 31366082
- PMCID: PMC6724175
- DOI: 10.3390/plants8080256
Ethnobotanical Knowledge in Sete Cidades, Azores Archipelago: First Ethnomedicinal Report
Abstract
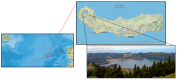
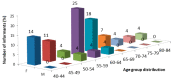
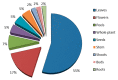
Knowledge about folk medicines is limited to elder community members of remote communities, like Sete Cidades in the Azores. The Azores, 1300 km west of Portugal, are nine volcanic islands, totalling 2330 km2 of land dispersed by 173,200 km2 in the North Atlantic Ocean. The present study aims to scientifically document the uses of plant species for medicinal purposes, in the Sete Cidades. Twenty-eight community members from 40 to 84 years of age, of whom half were 55 to 64 years old, were interviewed. Twenty-nine taxa were reported as being used for medicinal purposes, ten of which have not been previously reported for ethnomedicinal use in Portugal, with a first record of the use of Morella faya. Leaves were the most used plant part (55%), and decoction the most common preparation mode. The five reported taxa with both the highest use value (0.71-0.25) and relative frequency of citation (0.14-0.11) were Clinopodium menthifolium subsp. ascendens, Aloysia citriodora, Mentha x piperita, Citrus limon and Rosmarinus officinalis. The traditional uses of some of the reported plants are supported by scientific studies, confirming their ethnomedicinal value and the need to preserve local knowledge of folk medicine practices.
Keywords: Azores; Clinopodium menthifolium subsp. ascendens; Morella faya; ethnobotany; ethnomedicine; medicinal plants; plant diversity; use value.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Traditional uses of medicinal plants practiced by the indigenous communities at Mohmand Agency, FATA, Pakistan.J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2018 Jan 9;14(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13002-017-0204-5. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2018. PMID: 29316948 Free PMC article.
-
Ethnobotany of medicinal plants used in Antakya: A multicultural district in Hatay Province of Turkey.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Nov 4;174:118-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.07.042. Epub 2015 Jul 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26239155
-
Sete Cidades and Furnas lake eutrophication (São Miguel, Azores): analysis of long-term monitoring data and remediation measures.Sci Total Environ. 2015 Jul 1;520:168-86. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.03.052. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Sci Total Environ. 2015. PMID: 25813970
-
Historical versus contemporary medicinal plant uses in the US Virgin Islands.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Nov 4;192:74-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.07.005. Epub 2016 Jul 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27377341 Review.
-
Traditional Knowledge of Medicinal Plants Used in the Northeastern Part of Morocco.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Aug 6;2021:6002949. doi: 10.1155/2021/6002949. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34512779 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ethnobotanical Inventory of Plants Used by Mountainous Rural Communities in NW Portugal.Plants (Basel). 2024 Oct 9;13(19):2824. doi: 10.3390/plants13192824. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409695 Free PMC article.
-
Remnants from the Past: From an 18th Century Manuscript to 21st Century Ethnobotany in Valle Imagna (Bergamo, Italy).Plants (Basel). 2023 Jul 24;12(14):2748. doi: 10.3390/plants12142748. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37514363 Free PMC article.
-
Monoterpenes and Sesquiterpenes of Essential Oils from Psidium Species and Their Biological Properties.Molecules. 2021 Feb 12;26(4):965. doi: 10.3390/molecules26040965. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33673039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using Medicinal Plants in Valmalenco (Italian Alps): From Tradition to Scientific Approaches.Molecules. 2020 Sep 10;25(18):4144. doi: 10.3390/molecules25184144. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32927742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soejarto D.D., Fong H.H., Tan G.T., Zhang H.J., Ma C.Y., Franzblau S.G., Gyllenhaal C., Riley M.C., Kadushin M.R., Pezzuto J.M., et al. Ethnobotany/ethnopharmacology and mass bioprospecting: Issues on intellectual property and benefit-sharing. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005;100:15–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2005.05.031. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pardo-de-Santayana M., Pieroni A., Puri R.K. The ethnobotany of Europe: Past and present. In: Pardo-de-Santayana M., Pieroni A., Puri R.K., editors. Ethnobotany in the new Europe: People, Health and Wild Plant Resources. Berghahn Books; New York, NY, USA: 2013. pp. 1–15.
-
- WHO Traditional Medicine Strategy: 2014–2023. [(accessed on 12 April 2019)];2013 Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/92455/9789241506090_eng.....
-
- WHO, Fact sheet N° 134. [(accessed on 13 April 2019)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/2003/fs134/en/
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

