Preclinical Evidence of STAT3 Inhibitor Pacritinib Overcoming Temozolomide Resistance via Downregulating miR-21-Enriched Exosomes from M2 Glioblastoma-Associated Macrophages
- PMID: 31269723
- PMCID: PMC6678764
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8070959
Preclinical Evidence of STAT3 Inhibitor Pacritinib Overcoming Temozolomide Resistance via Downregulating miR-21-Enriched Exosomes from M2 Glioblastoma-Associated Macrophages
Abstract
Background: The tumor microenvironment (TME) plays a crucial role in virtually every aspect of tumorigenesis of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). A dysfunctional TME promotes drug resistance, disease recurrence, and distant metastasis. Recent evidence indicates that exosomes released by stromal cells within the TME may promote oncogenic phenotypes via transferring signaling molecules such as cytokines, proteins, and microRNAs.
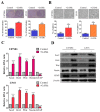
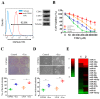
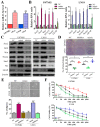
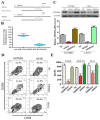
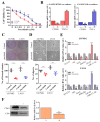
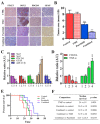
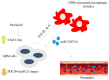
Results: In this study, clinical GBM samples were collected and analyzed. We found that GBM-associated macrophages (GAMs) secreted exosomes which were enriched with oncomiR-21. Coculture of GAMs (and GAM-derived exosomes) and GBM cell lines increased GBM cells' resistance against temozolomide (TMZ) by upregulating the prosurvival gene programmed cell death protein 4 (PDCD4) and stemness markers SRY (sex determining region y)-box 2 (Sox2), signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), Nestin, and miR-21-5p and increasing the M2 cytokines interleukin 6 (IL-6) and transforming growth factor beta 1(TGF-β1) secreted by GBM cells, promoting the M2 polarization of GAMs. Subsequently, pacritinib treatment suppressed GBM tumorigenesis and stemness; more importantly, pacritinib-treated GBM cells showed a markedly reduced ability to secret M2 cytokines and reduced miR-21-enriched exosomes secreted by GAMs. Pacritinib-mediated effects were accompanied by a reduction of oncomiR miR-21-5p, by which the tumor suppressor PDCD4 was targeted. We subsequently established patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models where mice bore patient GBM and GAMs. Treatment with pacritinib and the combination of pacritinib and TMZ appeared to significantly reduce the tumorigenesis of GBM/GAM PDX mice as well as overcome TMZ resistance and M2 polarization of GAMs.
Conclusion: In summation, we showed the potential of pacritinib alone or in combination with TMZ to suppress GBM tumorigenesis via modulating STAT3/miR-21/PDCD4 signaling. Further investigations are warranted for adopting pacritinib for the treatment of TMZ-resistant GBM in clinical settings.
Keywords: GBM-associated macrophages (GAMs); STAT3 inhibitor; exosomes; glioblastoma multiforme (GBM); oncomiR-21; tumor microenvironment (TME).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no potential financial competing interests from which they may in any way gain or lose financially from the publication of this manuscript presently or in the future. Additionally, no nonfinancial competing interests are involved in the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulating lncRNA SNHG15/CDK6/miR-627 circuit by palbociclib, overcomes temozolomide resistance and reduces M2-polarization of glioma associated microglia in glioblastoma multiforme.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Aug 28;38(1):380. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1371-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31462285 Free PMC article.
-
miR-519a enhances chemosensitivity and promotes autophagy in glioblastoma by targeting STAT3/Bcl2 signaling pathway.J Hematol Oncol. 2018 May 29;11(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0618-0. J Hematol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29843746 Free PMC article.
-
The JAK2/STAT3 inhibitor pacritinib effectively inhibits patient-derived GBM brain tumor initiating cells in vitro and when used in combination with temozolomide increases survival in an orthotopic xenograft model.PLoS One. 2017 Dec 18;12(12):e0189670. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189670. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29253028 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting Microglial Functions for the Treatment of Glioblastoma.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2017;17(3):267-281. doi: 10.2174/1568009616666160813191240. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2017. PMID: 27528361 Review.
-
Temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma multiforme.Genes Dis. 2016 May 11;3(3):198-210. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2016.04.007. eCollection 2016 Sep. Genes Dis. 2016. PMID: 30258889 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overcoming Acquired Drug Resistance to Cancer Therapies through Targeted STAT3 Inhibition.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 1;24(5):4722. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054722. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lucanthone Targets Lysosomes to Perturb Glioma Proliferation, Chemoresistance and Stemness, and Slows Tumor Growth In Vivo.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 14;12:852940. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.852940. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35494072 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of miRNA in Glioblastoma Tumor Cell Communication: Diplomatic and Aggressive Negotiations.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 12;21(6):1950. doi: 10.3390/ijms21061950. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32178454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Multifaceted Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Glioblastoma: microRNA Nanocarriers for Disease Progression and Gene Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jun 29;13(7):988. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13070988. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34210109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Origin, activation, and targeted therapy of glioma-associated macrophages.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 6;13:974996. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.974996. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275720 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Skog J., Würdinger T., Van Rijn S., Meijer D.H., Gainche L., Curry W.T., Carter B.S., Krichevsky A.M., Breakefield X.O., Sena-Esteves M., et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008;10:1470–1476. doi: 10.1038/ncb1800. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

