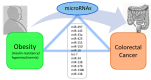
Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Colorectal Cancer: Could miRNA Dysregulation Play A Role?
- PMID: 31207998
- PMCID: PMC6628223
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20122922
Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Colorectal Cancer: Could miRNA Dysregulation Play A Role?
Abstract
Obesity is associated with insulin resistance and low-grade inflammation. Insulin resistance is a risk factor for cancer. A recent chapter in epigenetics is represented by microRNAs (miRNAs), which post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression. Dysregulated miRNA profiles have been associated with diseases including obesity and cancer. Herein we report dysregulated miRNAs in obesity both in animal models and in humans, and we also document dysregulated miRNAs in colorectal cancer (CRC), as example of an obesity-related cancer. Some of the described miRNAs are found to be similarly dysregulated both in obesity, insulin resistance (IR), and CRC. Thus, we present miRNAs as a potential molecular link between obesity and CRC onset and development, giving a new perspective on the role of miRNAs in obesity-associated cancers.
Keywords: cancer; colorectal cancer; inflammation; insulin resistance; microRNA; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-107: a toll-like receptor-regulated miRNA dysregulated in obesity and type II diabetes.J Leukoc Biol. 2012 Sep;92(3):521-7. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0312160. Epub 2012 May 29. J Leukoc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22645244 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in the prognosis and therapy of colorectal cancer: From bench to bedside.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jul 21;24(27):2949-2973. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i27.2949. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30038463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissecting miRNA signature in colorectal cancer progression and metastasis.Cancer Lett. 2021 Mar 31;501:66-82. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.12.025. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 33385486 Review.
-
Expression of miRNA in obesity and insulin resistance: a review.Endokrynol Pol. 2021;72(1):73-80. doi: 10.5603/EP.a2021.0002. Endokrynol Pol. 2021. PMID: 33749820 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in colorectal cancer: role in metastasis and clinical perspectives.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Dec 7;20(45):17011-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17011. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25493013 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of microRNAs Derived from Transposable Elements in the Macaca mulatta (Rhesus Monkey) Genome.Genes (Basel). 2023 Oct 24;14(11):1984. doi: 10.3390/genes14111984. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38002927 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of miRNAs in the Development, Proliferation, and Progression of Endometrial Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 15;24(14):11489. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411489. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin resistance and inflammation mediate the association of abdominal obesity with colorectal cancer risk.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 3;13:983160. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.983160. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36407320 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals in Human Fetal Growth.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 20;21(4):1430. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041430. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32093249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Absolute Quantification of Selected microRNAs Expression in Endometrial Cancer by Digital PCR.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 14;25(6):3286. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063286. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542261 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu Y., Han Z.P., Zhang S.S., Jing Y.Y., Bu X.X., Wang C.Y., Sun K., Jiang G.C., Zhao X., Li R., et al. Effects of inflammatory factors on mesenchymal stem cells and their role in the promotion of tumor angiogenesis in colon cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2011;286:25007–25015. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.213108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical