Circulating miR-20a and miR-26a as Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 31127907
- PMCID: PMC6857886
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.5.1453
Circulating miR-20a and miR-26a as Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer
Abstract
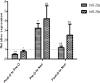
Objective: Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs), present in body fluids, have been considering importance as cancer biomarkers. The primary aim of this study was to assess whether circulatory miR-20a and miR-26a can be used as diagnostic biomarkers in prostate cancer (PCa). Methods: Relative expression miR-20a and miR-26a has been assessed in 40 patients with PCa and 40 non-cancerous volunteer. Sample Collection of patients was performed before and one week after prostatectomy. Total RNA was extracted from serum and miR-20a and miR-26a expressions were quantified by using Real-Time PCR method. Results: miR-20a was significantly up-regulated in pre-operation serum samples of PCa patients compared to the serum samples of non-cancerous controls, however, in post-operation samples no significant differences was showed. miR-26a level was not significantly decreased in pre and post-operation serum samples compared to the serum samples of controls. However, the expression level ratios of both miR-20a and miR-26a were insignificantly decreased when post-operation serum samples compared to pre-operation ones. Conclusion: Decrement of circulating miR-20a and miR-26a in patients after surgery may reflect the tumoral origin of those microRNAs and the results may use for tumor remnant monitoring after prostatectomy.
Keywords: Prostate cancer; circulatory microRNAs; miR-20a; miR-26a.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating miR-26a and miR-21 as biomarkers for glioblastoma multiform.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2019 Mar;66(2):261-265. doi: 10.1002/bab.1707. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30408234
-
Circulating microRNAs in plasma before and after radical prostatectomy.Urol Oncol. 2019 Nov;37(11):814.e1-814.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2019.07.001. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Urol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31421994 Free PMC article.
-
The correlation of circulating pro-angiogenic miRNAs' expressions with disease risk, clinicopathological features, and survival profiles in gastric cancer.Cancer Med. 2018 Aug;7(8):3773-3791. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1618. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 30003708 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of microRNA dysregulation in the development of prostate cancer.Reproduction. 2017 Oct;154(4):R81-R97. doi: 10.1530/REP-17-0322. Reproduction. 2017. PMID: 28878093 Review.
-
miRNAs as novel biomarkers in the management of prostate cancer.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017 May 1;55(5):715-736. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2015-1073. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017. PMID: 26751899 Review.
Cited by
-
Serum MicroRNA-137 Serves as a Novel Biomarker for Cerebral Atherosclerosis Diagnosis and Cerebrovascular Event Prediction.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 1;78(2):302-307. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001058. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34050091 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-26a represses pancreatic cancer cell malignant behaviors by targeting E2F7.Discov Oncol. 2021 Nov 27;12(1):55. doi: 10.1007/s12672-021-00448-z. Discov Oncol. 2021. PMID: 35201478 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA in prostate cancer: from biogenesis to applicative potential.BMC Urol. 2024 Nov 6;24(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s12894-024-01634-1. BMC Urol. 2024. PMID: 39506720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LINC01089 Blocks the Proliferation and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer Cells via Regulating miR-27b-3p/HOXA10 Axis.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Aug 19;13:8251-8260. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S256148. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32884303 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of miR-1826 in Prostate Cancer and Its Regulatory Effect on Tumor Progression.Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Aug 13;14:4467-4475. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S295125. eCollection 2021. Onco Targets Ther. 2021. PMID: 34413652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Backer H. Prostate cancer screening:exploring the debate. Permanente J. 1999;3:330–40.
-
- Brase JC, Johannes M, Schlomm T, et al. Circulating miRNAs are correlated with tumor progression in prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 2011;128:608–16. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical