Exosomal release through TRPML1-mediated lysosomal exocytosis is required for adipogenesis
- PMID: 30711251
- PMCID: PMC9883805
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.01.115
Exosomal release through TRPML1-mediated lysosomal exocytosis is required for adipogenesis
Abstract
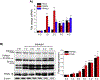
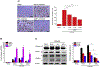
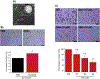
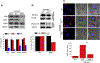
The lysosomal Ca2+ permeable channel TRPML1 (MCOLN1) plays key roles in lysosomal membrane trafficking, including the fusion of late endosomes to lysosomes and lysosomal exocytosis, both of which are essential for release of exosomes into the extracellular milieu. Multiple lines of evidence indicate that the contents of adipocyte-derived exosomes mediate diverse cellular responses, including adipogenic differentiation. In this study, we aimed to define the potential roles of TRPML1 in lysosomal membrane trafficking during adipogenesis and in exosomal release. In response to adipogenic stimuli, the endogenous TRPML1 expression in OP9 pre-adipocytes was increased in a time-dependent manner, and the acute deletion of TRPML1 reduced lipid synthesis and expression of differentiation-related marker genes. Notably, mature adipocyte-derived exosomes were found to be necessary for adipogenesis and were dependent on TRPML1-mediated lysosomal exocytosis. Taken together, our findings indicate that TRPML1 mediates diverse roles in adipocyte differentiation and exosomal release. Further, we propose that TRPML1 should be considered as a regulator of obesity-related diseases.
Keywords: Adipogenesis; Exosome; Lysosomal exocytosis; TRPML1.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Control of lysosomal TRPML1 channel activity and exosome release by acid ceramidase in mouse podocytes.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019 Sep 1;317(3):C481-C491. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00150.2019. Epub 2019 Jul 3. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31268777 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal podocyte TRPML1 channel activity and exosome release in mice with podocyte-specific Asah1 gene deletion.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021 Feb;1866(2):158856. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158856. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021. PMID: 33221496 Free PMC article.
-
A TRP channel in the lysosome regulates large particle phagocytosis via focal exocytosis.Dev Cell. 2013 Sep 16;26(5):511-24. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.08.003. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Dev Cell. 2013. PMID: 23993788 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosomal Exocytosis, Exosome Release and Secretory Autophagy: The Autophagic- and Endo-Lysosomal Systems Go Extracellular.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 8;21(7):2576. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072576. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32276321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRPML2 and mucolipin evolution.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;222:647-58. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-54215-2_25. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24756724 Review.
Cited by
-
The emerging roles and mechanisms of exosomal non-coding RNAs in the mutual regulation between adipose tissue and other related tissues in obesity and metabolic diseases.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 18;13:975334. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.975334. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36060952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Ceramides and Lysosomes in Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis, Cargo Sorting and Release.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 5;23(23):15317. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315317. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Machinery of Exosomes: Biogenesis, Release, and Uptake.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 10;24(2):1337. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021337. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles as Novel Drug-Delivery Systems through Intracellular Communications.Membranes (Basel). 2022 May 25;12(6):550. doi: 10.3390/membranes12060550. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35736256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the regulation of adipogenesis and lipid metabolism by exosomal ncRNAs and their role in related metabolic diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Sep 18;11:1173904. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1173904. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37791070 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

