Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017
- PMID: 30496104
- PMCID: PMC6227754
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7
Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017
Erratum in
-
Department of Error.Lancet. 2019 Jun 22;393(10190):e44. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31047-5. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 31232377 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2017 (GBD 2017) includes a comprehensive assessment of incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability (YLDs) for 354 causes in 195 countries and territories from 1990 to 2017. Previous GBD studies have shown how the decline of mortality rates from 1990 to 2016 has led to an increase in life expectancy, an ageing global population, and an expansion of the non-fatal burden of disease and injury. These studies have also shown how a substantial portion of the world's population experiences non-fatal health loss with considerable heterogeneity among different causes, locations, ages, and sexes. Ongoing objectives of the GBD study include increasing the level of estimation detail, improving analytical strategies, and increasing the amount of high-quality data.
Methods: We estimated incidence and prevalence for 354 diseases and injuries and 3484 sequelae. We used an updated and extensive body of literature studies, survey data, surveillance data, inpatient admission records, outpatient visit records, and health insurance claims, and additionally used results from cause of death models to inform estimates using a total of 68 781 data sources. Newly available clinical data from India, Iran, Japan, Jordan, Nepal, China, Brazil, Norway, and Italy were incorporated, as well as updated claims data from the USA and new claims data from Taiwan (province of China) and Singapore. We used DisMod-MR 2.1, a Bayesian meta-regression tool, as the main method of estimation, ensuring consistency between rates of incidence, prevalence, remission, and cause of death for each condition. YLDs were estimated as the product of a prevalence estimate and a disability weight for health states of each mutually exclusive sequela, adjusted for comorbidity. We updated the Socio-demographic Index (SDI), a summary development indicator of income per capita, years of schooling, and total fertility rate. Additionally, we calculated differences between male and female YLDs to identify divergent trends across sexes. GBD 2017 complies with the Guidelines for Accurate and Transparent Health Estimates Reporting.
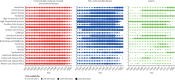
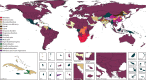
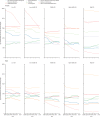
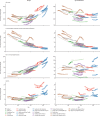
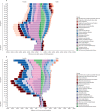
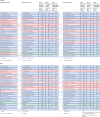
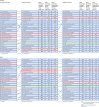
Findings: Globally, for females, the causes with the greatest age-standardised prevalence were oral disorders, headache disorders, and haemoglobinopathies and haemolytic anaemias in both 1990 and 2017. For males, the causes with the greatest age-standardised prevalence were oral disorders, headache disorders, and tuberculosis including latent tuberculosis infection in both 1990 and 2017. In terms of YLDs, low back pain, headache disorders, and dietary iron deficiency were the leading Level 3 causes of YLD counts in 1990, whereas low back pain, headache disorders, and depressive disorders were the leading causes in 2017 for both sexes combined. All-cause age-standardised YLD rates decreased by 3·9% (95% uncertainty interval [UI] 3·1-4·6) from 1990 to 2017; however, the all-age YLD rate increased by 7·2% (6·0-8·4) while the total sum of global YLDs increased from 562 million (421-723) to 853 million (642-1100). The increases for males and females were similar, with increases in all-age YLD rates of 7·9% (6·6-9·2) for males and 6·5% (5·4-7·7) for females. We found significant differences between males and females in terms of age-standardised prevalence estimates for multiple causes. The causes with the greatest relative differences between sexes in 2017 included substance use disorders (3018 cases [95% UI 2782-3252] per 100 000 in males vs s1400 [1279-1524] per 100 000 in females), transport injuries (3322 [3082-3583] vs 2336 [2154-2535]), and self-harm and interpersonal violence (3265 [2943-3630] vs 5643 [5057-6302]).
Interpretation: Global all-cause age-standardised YLD rates have improved only slightly over a period spanning nearly three decades. However, the magnitude of the non-fatal disease burden has expanded globally, with increasing numbers of people who have a wide spectrum of conditions. A subset of conditions has remained globally pervasive since 1990, whereas other conditions have displayed more dynamic trends, with different ages, sexes, and geographies across the globe experiencing varying burdens and trends of health loss. This study emphasises how global improvements in premature mortality for select conditions have led to older populations with complex and potentially expensive diseases, yet also highlights global achievements in certain domains of disease and injury.
Funding: Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.Lancet. 2020 Oct 17;396(10258):1204-1222. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30925-9. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 33069326 Free PMC article.
-
Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Lancet. 2024 May 18;403(10440):2133-2161. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00757-8. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Lancet. 2024. PMID: 38642570 Free PMC article.
-
The burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors by state in the USA, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Lancet. 2024 Dec 7;404(10469):2314-2340. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)01446-6. Lancet. 2024. PMID: 39645376 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Undernutrition as a risk factor for tuberculosis disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 11;6(6):CD015890. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015890.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38860538 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Community awareness initiative about antimicrobial resistance: An educational intervention by medical undergraduates.J Educ Health Promot. 2024 Aug 29;13:321. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_1735_23. eCollection 2024. J Educ Health Promot. 2024. PMID: 39429841 Free PMC article.
-
B-Cell Targeted Therapies in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis and Incidence of Headache: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Pers Med. 2022 Sep 8;12(9):1474. doi: 10.3390/jpm12091474. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36143259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the Association of Metabolic Biomarkers With Knee Cartilage Composition and Structural Abnormalities Using MRI: A Pilot Study.Cartilage. 2021 Dec;13(1_suppl):630S-638S. doi: 10.1177/1947603520946376. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Cartilage. 2021. PMID: 32757831 Free PMC article.
-
Retrotransposon insertions associated with risk of neurologic and psychiatric diseases.EMBO Rep. 2023 Jan 9;24(1):e55197. doi: 10.15252/embr.202255197. Epub 2022 Nov 11. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 36367221 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and validation of biomarkers to aid the development of safe and effective pain therapeutics: challenges and opportunities.Nat Rev Neurol. 2020 Jul;16(7):381-400. doi: 10.1038/s41582-020-0362-2. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Nat Rev Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32541893 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nino F. United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. UNDP. http://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/sustainable-development-goals.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH110163/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RG/13/13/30194/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MC_U147585819/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12011/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A620_1014/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN271201300071C/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC25195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/M015084/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 201900/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P01 HD031921/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- SCAF/15/02/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MR/L003120/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 206471/Z/17/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 AG009740/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG047845/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK106515/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

