A CK1α Activator Penetrates the Brain and Shows Efficacy Against Drug-resistant Metastatic Medulloblastoma
- PMID: 30487124
- PMCID: PMC7142219
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1319
A CK1α Activator Penetrates the Brain and Shows Efficacy Against Drug-resistant Metastatic Medulloblastoma
Abstract
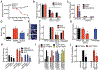
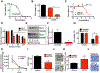
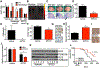
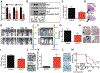
Purpose: Although most children with medulloblastoma are cured of their disease, Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) subgroup medulloblastoma driven by TRP53 mutations is essentially lethal. Casein kinase 1α (CK1α) phosphorylates and destabilizes GLI transcription factors, thereby inhibiting the key effectors of SHH signaling. We therefore tested a second-generation CK1α activator against TRP53-mutant, MYCN-amplified medulloblastoma.
Experimental design: The ability of this CK1α activator to block SHH signaling was determined in vitro using GLI reporter cells, granular precursor primary cultures, and PATCHED1 (PTCH1)-mutant sphere cultures. While in vivo efficacy was tested using 2 different medulloblastoma mouse models: PTCH1 and ND2:SMOA1. Finally, the clinical relevance of CK1α activators was demonstrated using a TRP53-mutant, MYCN-amplified patient-derived xenograft.
Results: SSTC3 inhibited SHH activity in vitro, acting downstream of the vismodegib target SMOOTHENED (SMO), and reduced the viability of sphere cultures derived from SHH medulloblastoma. SSTC3 accumulated in the brain, inhibited growth of SHH medulloblastoma tumors, and blocked metastases in a genetically engineered vismodegib-resistant mouse model of SHH medulloblastoma. Importantly, SSTC3 attenuated growth and metastasis of orthotopic patient-derived TRP53-mutant, MYCN-amplified, SHH subgroup medulloblastoma xenografts, increasing overall survival.
Conclusions: Using a newly described small-molecule, SSTC3, we show that CK1a activators could address a significant unmet clinical need for patients with SMO inhibitor-resistant medulloblastoma, including those harboring mutations in TRP53.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
D.J. Robbins is an employee of and has ownership interests (including patents) at StemSynergy Therapeutics, Inc. D. Orton has ownership interests (including patents) in StemSynergy Therapeutics, Inc. and reports receiving commercial research grants from NIH. M.F. Roussel is an employee of University of Tennessee. W.A. Weiss has ownership interests (including patents) in StemSynergy Therapeutics, Inc. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome sequencing of SHH medulloblastoma predicts genotype-related response to smoothened inhibition.Cancer Cell. 2014 Mar 17;25(3):393-405. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.02.004. Cancer Cell. 2014. PMID: 24651015 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of WNT signaling attenuates self-renewal of SHH-subgroup medulloblastoma.Oncogene. 2017 Nov 9;36(45):6306-6314. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.232. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28714964 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of apoptotic genes and downregulation of target genes of Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway in DAOY medulloblastoma cell line treated with arsenic trioxide.J Chemother. 2024 Oct;36(6):506-519. doi: 10.1080/1120009X.2023.2294574. Epub 2023 Dec 22. J Chemother. 2024. PMID: 38130211
-
The SHH/GLI signaling pathway: a therapeutic target for medulloblastoma.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020 Nov;24(11):1159-1181. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2020.1823967. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020. PMID: 32990091 Review.
-
SHH inhibitors for the treatment of medulloblastoma.Expert Rev Neurother. 2015;15(7):763-70. doi: 10.1586/14737175.2015.1052796. Epub 2015 May 31. Expert Rev Neurother. 2015. PMID: 26027634 Review.
Cited by
-
Casein kinase 1α inhibits p53 downstream of MDM2‑mediated autophagy and apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia.Oncol Rep. 2020 Nov;44(5):1895-1904. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7760. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32901886 Free PMC article.
-
ABT-737 suppresses aberrant Hedgehog pathway and overcomes resistance to smoothened antagonists by blocking Gli.Med Oncol. 2022 Sep 7;39(12):188. doi: 10.1007/s12032-022-01794-w. Med Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36071246
-
A Druggable UHRF1/DNMT1/GLI Complex Regulates Sonic Hedgehog-Dependent Tumor Growth.Mol Cancer Res. 2022 Nov 3;20(11):1598-1610. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-22-0182. Mol Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35925047 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitors as Targeted Cancer Therapy and Strategies to Overcome Drug Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 3;23(3):1733. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031733. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CK1α Activator Pyrvinium Enhances the Catalytic Efficiency (kcat/Km) of CK1α.Biochemistry. 2019 Dec 24;58(51):5102-5106. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00891. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31820934 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuzan-Fischer CM, Guerreiro Stucklin AS, Taylor MD. Advances in genomics explain medulloblastoma behavior at the bedside. Neurosurgery 2017;64:21–6. - PubMed
-
- MacDonald TJ, Rood BR, Santi MR, Vezina G, Bingaman K, Cogen PH, et al. Advances in the diagnosis, molecular genetics, and treatment of pediatric embryonal CNS tumors. Oncologist 2003;8:174–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

