Cardiac Troponins for the Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction in Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 30371308
- PMCID: PMC6404905
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.117.008032
Cardiac Troponins for the Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
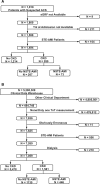
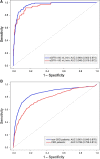
Background Patients with chronic kidney disease ( CKD ) are at high risk of myocardial infarction. Cardiac troponins are the biomarkers of choice for the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction ( AMI ) without ST -segment elevation ( NSTE ). In patients with CKD , troponin levels are often chronically elevated, which reduces their diagnostic utility when NSTE - AMI is suspected. The aim of this study was to derive a diagnostic algorithm for serial troponin measurements in patients with CKD and suspected NSTE - AMI . Methods and Results Two cohorts, 1494 patients from a prospective cohort study with high-sensitivity troponin I (hs- cTnI ) measurements and 7059 cases from a clinical registry with high-sensitivity troponin T (hs- cTnT ) measurements, were analyzed. The prospective cohort comprised 280 CKD patients (estimated glomerular filtration rate <60 mL/min/1.73 m2). The registry data set contained 1581 CKD patients. In both cohorts, CKD patients were more likely to have adjudicated NSTE - AMI than non- CKD patients. The specificities of hs- cTnI and hs- cTnT to detect NSTE - AMI were reduced with CKD (0.82 versus 0.91 for hs- cTnI and 0.26 versus 0.73 for hs- cTnT ) but could be restored by applying optimized cutoffs to either the first or a second measurement after 3 hours. The best diagnostic performance was achieved with an algorithm that incorporates serial measurements and rules in or out AMI in 69% (hs- cTnI ) and 55% (hs- cTnT ) of CKD patients. Conclusions The diagnostic performance of high-sensitivity cardiac troponins in patients with CKD with suspected NSTE - AMI is improved by use of an algorithm based on admission troponin and dynamic changes in troponin concentration.
Keywords: biomarker; chronic kidney disease; cohort study; decision aids; non‐ST‐segment elevation acute coronary syndrome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Cardiac Troponins in Predicting Adverse Outcomes in Acute Coronary Syndrome With Renal Dysfunction.Cureus. 2023 Oct 16;15(10):e47104. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47104. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38022315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-sensitive cardiac troponin for the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in different chronic kidney disease stages.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 Feb 17;21(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01746-0. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 33596833 Free PMC article.
-
Superiority of high sensitivity cardiac troponin T vs. I for long-term prognostic value in patients with chest pain; data from the Akershus cardiac Examination (ACE) 3 study.Clin Biochem. 2020 Apr;78:10-17. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2019.12.016. Epub 2019 Dec 31. Clin Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31899280
-
Clinical Evaluation of a New High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin I Assay for Diagnosis and Risk Assessment of Patients with Suspected Acute Myocardial Infarction.Cardiology. 2021;146(2):172-178. doi: 10.1159/000512185. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Cardiology. 2021. PMID: 33461202 Free PMC article.
-
Use and interpretation of high sensitivity cardiac troponins in patients with chronic kidney disease with and without acute myocardial infarction.Clin Biochem. 2015 Mar;48(4-5):247-53. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2015.01.004. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Clin Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25617663 Review.
Cited by
-
Kidney function-specific cut-off values of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T for the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction.Clin Kidney J. 2024 Aug 23;17(9):sfae247. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfae247. eCollection 2024 Sep. Clin Kidney J. 2024. PMID: 39246629 Free PMC article.
-
Ambient Mass Spectrometry and Machine Learning-Based Diagnosis System for Acute Coronary Syndrome.Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2024;13(1):A0147. doi: 10.5702/massspectrometry.A0147. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2024. PMID: 39005641 Free PMC article.
-
Inconsistent Findings of Cardiac Troponin T and I in Clinical Routine Diagnostics: Factors of Influence.J Clin Med. 2021 Jul 16;10(14):3148. doi: 10.3390/jcm10143148. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34300313 Free PMC article.
-
Value of the high-sensitivity troponin T assay for diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in patients with and without renal insufficiency.Ren Fail. 2020 Nov;42(1):1142-1151. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2020.1845732. Ren Fail. 2020. PMID: 33183098 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Cardiac Troponins in Predicting Adverse Outcomes in Acute Coronary Syndrome With Renal Dysfunction.Cureus. 2023 Oct 16;15(10):e47104. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47104. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38022315 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roffi M, Patrono C, Collet J‐P, Mueller C, Valgimigli M, Andreotti F, Bax JJ, Borger MA, Brotons C, Chew DP, Gencer B, Hasenfuss G, Kjeldsen K, Lancellotti P, Landmesser U, Mehilli J, Mukherjee D, Storey RF, Windecker S, Baumgartner H, Gaemperli O, Achenbach S, Agewall S, Badimon L, Baigent C, Bueno H, Bugiardini R, Carerj S, Casselman F, Cuisset T, Erol Ç, Fitzsimons D, Halle M, Hamm C, Hildick‐Smith D, Huber K, Iliodromitis E, James S, Lewis BS, Lip GYH, Piepoli MF, Richter D, Rosemann T, Sechtem U, Steg PG, Vrints C, Luis Zamorano J;. 2015 ESC guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST‐segment elevation: Task Force for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST‐segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2016;37:267–315. - PubMed
-
- Wong JA, Goodman SG, Yan RT, Wald R, Bagnall AJ, Welsh RC, Wong GC, Kornder J, Eagle KA, Steg PG, Yan AT; Canadian Acute Coronary Syndromes I and II, and Canadian Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE/GRACE) Investigators . Temporal management patterns and outcomes of non‐ST elevation acute coronary syndromes in patients with kidney dysfunction. Eur Heart J. 2009;30:549–557. - PubMed
-
- Twerenbold R, Wildi K, Jaeger C, Gimenez MR, Reiter M, Reichlin T, Walukiewicz A, Gugala M, Krivoshei L, Marti N, Moreno Weidmann Z, Hillinger P, Puelacher C, Rentsch K, Honegger U, Schumacher C, Zurbriggen F, Freese M, Stelzig C, Campodarve I, Bassetti S, Osswald S, Mueller C. Optimal cutoff levels of more sensitive cardiac troponin assays for the early diagnosis of myocardial infarction in patients with renal dysfunction. Circulation. 2015;131:2041–2050. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chenevier‐Gobeaux C, Meune C, Freund Y, Wahbi K, Claessens Y‐E, Doumenc B, Zuily S, Riou B, Ray P. Influence of age and renal function on high‐sensitivity cardiac troponin T diagnostic accuracy for the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 2013;111:1701–1707. - PubMed
-
- Keller T, Zeller T, Peetz D, Tzikas S, Roth A, Czyz E, Bickel C, Baldus S, Warnholtz A, Fröhlich M, Sinning CR, Eleftheriadis MS, Wild PS, Schnabel RB, Lubos E, Jachmann N, Genth‐Zotz S, Post F, Nicaud V, Tiret L, Lackner KJ, Münzel TF, Blankenberg S. Sensitive troponin I assay in early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:868–877. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

