Anti-LL37 Antibodies Are Present in Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) Patients: New Biomarkers in PsA
- PMID: 30279686
- PMCID: PMC6154218
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01936
Anti-LL37 Antibodies Are Present in Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) Patients: New Biomarkers in PsA
Abstract
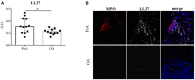
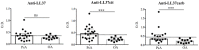
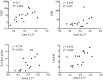
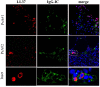
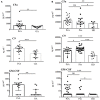
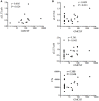
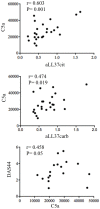
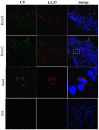
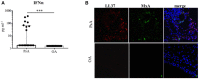
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic inflammatory arthritis associated with psoriasis. A third of psoriatic patients develop PsA via unknown mechanisms. No reliable diagnostic markers are available for PsA, or prognostic biomarkers for PsA development in psoriasis. We previously uncovered a pro-inflammatory role for cathelicidin LL37 in lesional psoriasis skin. LL37 binds nucleic acids and stimulates plasmacytoid/myeloid dendritic cells (pDC, mDCs) to secrete type I interferon (IFN-I) and pro-inflammatory factors. LL37 becomes an autoantigen for psoriatic Th1-Th17/CD8 T cells. Anti-LL37 antibodies were detected in systemic lupus erythematosus, an autoimmune disease characterized by neutrophil-extracellular-traps release (NETosis) in target organs. LL37 can be substrate of irreversible post-translational modifications, citrullination or carbamylation, linked to neutrophil activity. Here we analyzed inflammatory factors, included LL37, in PsA and psoriasis plasma and PsA synovial fluids (SF)/biopsies. We show that LL37 (as a product of infiltrating neutrophils) and autoantibodies to LL37 are elevated in PsA, but not OA SF. Anti-LL37 antibodies correlate with clinical inflammatory markers. Anti-carbamylated/citrullinated-LL37 antibodies are present in PsA SF/plasma and, at lower extent, in psoriasis plasma, but not in controls. Plasma anti-carbamylated-LL37 antibodies correlate with PsA (DAS44) but not psoriasis (PASI) disease activity. Ectopic lymphoid structures, and deposition of immunoglobulin-(Ig)G-complexes (IC) co-localizing with infiltrating neutrophils, are observed in PsA and not OA synovial tissues (ST). Activated complement (C5a, C9), GM-CSF and IFN-I are up-regulated in PsA and not OA synovia and in PsA and psoriasis plasma but not in HD. C9 and GM-CSF levels in PsA SF correlate with clinical inflammatory markers and DAS44 (C9) and with anti-carbamylated/citrullinated-LL37 antibodies (GM-CSF and IFN-I). Thus, we uncover a role for LL37 as a novel PsA autoantibody target and correlation studies suggest participation of anti-LL37 antibodies to PsA pathogenesis. Notably, plasma antibodies to carbamylated-LL37, which correlate with DAS44, suggest their use as new disease activity markers. GM-CSF and complement C5a and C9 elevation may be responsible for autoantigens release by neutrophils and their modification, fueling inflammation and autoreactivity establishment. Finally, targeting GM-CSF, C5a, C9 can be beneficial in PsA.
Keywords: LL37; Psoriatic arthritis; autoantibodies complement; neutrophils; psoriasis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Complementary Effects of Carbamylated and Citrullinated LL37 in Autoimmunity and Inflammation in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 6;22(4):1650. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041650. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33562078 Free PMC article.
-
Native/citrullinated LL37-specific T-cells help autoantibody production in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 3;10(1):5851. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62480-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32245990 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Carbamylated LL37 Antibodies Promote Pathogenic Bone Resorption in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 14;12:715997. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.715997. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34594331 Free PMC article.
-
Current knowledge on autoantigens and autoantibodies in psoriasis.Scand J Immunol. 2020 Oct;92(4):e12945. doi: 10.1111/sji.12945. Scand J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32697368 Review.
-
Auto-reactions, autoimmunity and psoriatic arthritis.Autoimmun Rev. 2015 Dec;14(12):1142-6. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.08.003. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Autoimmun Rev. 2015. PMID: 26254734 Review.
Cited by
-
NETosis in Psoriatic Arthritis: Serum MPO-DNA Complex Level Correlates With Its Disease Activity.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 14;13:911347. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.911347. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35774788 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in transcriptional changes in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis skin with immunoglobulin gene enrichment in psoriatic arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024 Jan 4;63(1):218-225. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead195. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 37137278 Free PMC article.
-
Increased histone citrullination in juvenile idiopathic arthritis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 19;9:971121. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.971121. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36059852 Free PMC article.
-
Psoriasis and Antimicrobial Peptides.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 16;21(18):6791. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186791. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32947991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adaptive and Innate Immunity in Psoriasis and Other Inflammatory Disorders.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 26;10:1764. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01764. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31402919 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Conigliaro P, Triggianese P, Perricone C, Chimenti MS, Di Muzio G, Ballanti E, et al. . Restoration of peripheral blood natural killer and B cell levels in patients affected by rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis during etanercept treatment. Clin Exp Immunol. (2014) 177:234–43. 10.1111/cei.12335 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

