Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-Associated Factor Regulation of Nuclear Factor κB and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways
- PMID: 30140268
- PMCID: PMC6094638
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01849
Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-Associated Factor Regulation of Nuclear Factor κB and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways
Abstract
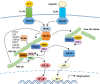
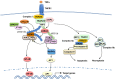
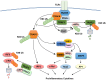
Tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)-associated factors (TRAFs) are a family of structurally related proteins that transduces signals from members of TNFR superfamily and various other immune receptors. Major downstream signaling events mediated by the TRAF molecules include activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). In addition, some TRAF family members, particularly TRAF2 and TRAF3, serve as negative regulators of specific signaling pathways, such as the noncanonical NF-κB and proinflammatory toll-like receptor pathways. Thus, TRAFs possess important and complex signaling functions in the immune system and play an important role in regulating immune and inflammatory responses. This review will focus on the role of TRAF proteins in the regulation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways.
Keywords: inflammation; mitogen-activated protein kinases; nuclear factor κB; toll-like receptors; tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor; tumor necrosis factor receptors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TNF receptor (TNFR)-associated factor (TRAF) 3 serves as an inhibitor of TRAF2/5-mediated activation of the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway by TRAF-binding TNFRs.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 22;102(8):2874-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500187102. Epub 2005 Feb 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15708970 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor (TRAF)-interacting protein (TRIP) negatively regulates the TRAF2 ubiquitin-dependent pathway by suppressing the TRAF2-sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) interaction.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 10;290(15):9660-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.609685. Epub 2015 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25716317 Free PMC article.
-
Differential requirements for tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor family proteins in CD40-mediated induction of NF-kappaB and Jun N-terminal kinase activation.J Biol Chem. 1999 Aug 6;274(32):22414-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.32.22414. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10428814
-
The Roles of TRAF3 in Immune Responses.Dis Markers. 2023 Feb 16;2023:7787803. doi: 10.1155/2023/7787803. eCollection 2023. Dis Markers. 2023. PMID: 36845015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting signaling factors for degradation, an emerging mechanism for TRAF functions.Immunol Rev. 2015 Jul;266(1):56-71. doi: 10.1111/imr.12311. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26085207 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isosteviol plays a protective role on hepatic ischemia and reperfusion injury in mice through MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway.Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan 23;9:66. doi: 10.21037/tgh-23-66. eCollection 2024. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39503028 Free PMC article.
-
Effects and mechanisms of natural alkaloids for prevention and treatment of osteoporosis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 23;13:1014173. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1014173. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36210805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skeletal muscle fibers play a functional role in host defense during sepsis in mice.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 1;11(1):7316. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86585-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33795743 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Key Pathways and Genes of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Specific Neutrophil Phenotype.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Aug 19;2019:9528584. doi: 10.1155/2019/9528584. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31531373 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF4 Inhibits the Apoptosis and Promotes the Proliferation of Breast Cancer Cells by Inhibiting the Ubiquitination of Spindle Assembly-Associated Protein Eg5.Front Oncol. 2022 May 25;12:855139. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.855139. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35692762 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

