IFNγ: signalling, epigenetics and roles in immunity, metabolism, disease and cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 29921905
- PMCID: PMC6340644
- DOI: 10.1038/s41577-018-0029-z
IFNγ: signalling, epigenetics and roles in immunity, metabolism, disease and cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
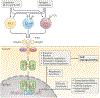
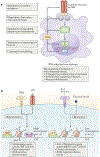
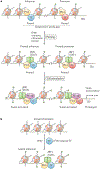
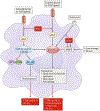
IFNγ is a cytokine with important roles in tissue homeostasis, immune and inflammatory responses and tumour immunosurveillance. Signalling by the IFNγ receptor activates the Janus kinase (JAK)-signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) pathway to induce the expression of classical interferon-stimulated genes that have key immune effector functions. This Review focuses on recent advances in our understanding of the transcriptional, chromatin-based and metabolic mechanisms that underlie IFNγ-mediated polarization of macrophages to an 'M1-like' state, which is characterized by increased pro-inflammatory activity and macrophage resistance to tolerogenic and anti-inflammatory factors. In addition, I describe the newly discovered effects of IFNγ on other leukocytes, vascular cells, adipose tissue cells, neurons and tumour cells that have important implications for autoimmunity, metabolic diseases, atherosclerosis, neurological diseases and immune checkpoint blockade cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
STAT1 as a novel therapeutical target in pro-atherogenic signal integration of IFNγ, TLR4 and IL-6 in vascular disease.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011 Aug;22(4):211-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2011.06.003. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011. PMID: 21752694 Review.
-
Downregulated SOCS1 expression activates the JAK1/STAT1 pathway and promotes polarization of macrophages into M1 type.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Nov;16(5):6405-6411. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7384. Epub 2017 Aug 29. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28901399
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms Governing Innate Inflammatory Responses.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2016 Jul;36(7):454-61. doi: 10.1089/jir.2016.0003. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2016. PMID: 27379867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pro-inflammatory cytokines negatively regulate PPARγ mediated gene expression in both human and murine macrophages via multiple mechanisms.Immunobiology. 2013 Nov;218(11):1336-44. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2013.06.011. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Immunobiology. 2013. PMID: 23870825
-
Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic disorders.Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):1939-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23770291 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging strategies in targeting tumor-resident myeloid cells for cancer immunotherapy.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Aug 28;15(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01335-y. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36031601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TLR2-induced CD8+ T-cell deactivation shapes dendritic cell differentiation in the bone marrow during sepsis.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 6;13:945409. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.945409. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36148245 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the causal association between rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of cervical cancer: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Jan 23;26(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03240-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38263277 Free PMC article.
-
IFN-γ and TNF-α drive a CXCL10+ CCL2+ macrophage phenotype expanded in severe COVID-19 lungs and inflammatory diseases with tissue inflammation.Genome Med. 2021 Apr 20;13(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13073-021-00881-3. Genome Med. 2021. PMID: 33879239 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent tailoring of MSC activation through genetic priming.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024 Aug 8;32(3):101316. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101316. eCollection 2024 Sep 12. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024. PMID: 39282077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Villarino AV, Kanno Y & O’Shea JJ Mechanisms and consequences of Jak-STAT signaling in the immune system. Nat. Immunol 18, 374–384 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Levy DE, Kessler DS, Pine R, Reich N & Darnell JE Jr. Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 2, 383–393 (1988). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

