Endoplasmic reticulum stress stimulates the release of extracellular vesicles carrying danger-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecules
- PMID: 29467921
- PMCID: PMC5805507
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.24158
Endoplasmic reticulum stress stimulates the release of extracellular vesicles carrying danger-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecules
Abstract
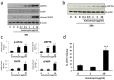
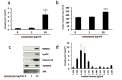
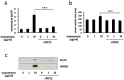
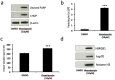
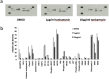
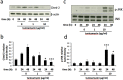
Disturbances in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) function lead to ER stress which, when severe or prolonged, may result in apoptosis. Severe ER stress has been implicated in several pathological conditions including pre-eclampsia, a multisystem disorder of pregnancy associated with the release of pro-inflammatory factors from the placenta into the maternal circulation. Here, we show that severe ER stress induced by two distinct mechanisms in BeWo choriocarcinoma cells leads to the release of extracellular vesicles (EVs) carrying pro-inflammatory damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecules. Co-treatment with the antioxidant pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate results in a reduction in ER stress-induced EV-associated DAMP release. We further demonstrate that severe ER stress is associated with changes in the expression of several stress-related proteins, notably Cited-2 and phosphorylated JNK. Together, these data indicate that severe ER stress-mediated release of EV-associated DAMPs may contribute to the heightened systemic maternal inflammatory response characteristic of pre-eclampsia and may also be relevant to other chronic inflammatory diseases which display elevated ER stress.
Keywords: ER stress; endoplasmic reticulum stress; extracellular vesicles; pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aggregated and Hyperstable Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns Are Released During ER Stress to Modulate Immune Function.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Sep 18;7:198. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00198. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31620439 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Large Extracellular Vesicles (Microparticles) in Endothelial Cell Dysfunction.Biomedicines. 2020 Oct 12;8(10):409. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8100409. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 33053883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocytes release ceramide-enriched pro-inflammatory extracellular vesicles in an IRE1α-dependent manner.J Lipid Res. 2016 Feb;57(2):233-45. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M063412. Epub 2015 Nov 30. J Lipid Res. 2016. PMID: 26621917 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellularly Released Calreticulin Induced by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Impairs Syncytialization of Cytotrophoblast Model BeWo Cells.Cells. 2021 May 24;10(6):1305. doi: 10.3390/cells10061305. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34073978 Free PMC article.
-
Immunothrombotic Activity of Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns and Extracellular Vesicles in Secondary Organ Failure Induced by Trauma and Sterile Insults.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 8;9:190. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00190. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29472928 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MHY1485 potentiates immunogenic cell death induction and anti-cancer immunity following irradiation.J Radiat Res. 2024 Mar 22;65(2):205-214. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrad107. J Radiat Res. 2024. PMID: 38330507 Free PMC article.
-
Preeclampsia and syncytiotrophoblast membrane extracellular vesicles (STB-EVs).Clin Sci (Lond). 2022 Dec 22;136(24):1793-1807. doi: 10.1042/CS20220149. Clin Sci (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36511102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-1 alpha and high mobility group box-1 secretion in polyinosinic:polycytidylic-induced colorectal cancer cells occur via RIPK1-dependent mechanism and participate in tumourigenesis.J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Mar;17(1):189-208. doi: 10.1007/s12079-022-00681-3. Epub 2022 May 9. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 35534784 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles: Potential impact on cardiovascular diseases.Adv Clin Chem. 2021;105:49-100. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2021.02.002. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Adv Clin Chem. 2021. PMID: 34809830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles and immunogenic stress in cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Oct 1;12(10):894. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04171-z. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34599143 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Seimon TA, Nadolski MJ, Liao X, Magallon J, Nguyen M, Feric NT, Koschinsky ML, Harkewicz R, Witztum JL, Tsimikas S, Golenbock D, Moore KJ, Tabas I. Atherogenic lipids and lipoproteins trigger CD36-TLR2-dependent apoptosis in macrophages undergoing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Metab. 2010;12:467–82. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

