A negative feedback regulation of MTORC1 activity by the lysosomal Ca2+ channel MCOLN1 (mucolipin 1) using a CALM (calmodulin)-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 29460684
- PMCID: PMC5846559
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1389822
A negative feedback regulation of MTORC1 activity by the lysosomal Ca2+ channel MCOLN1 (mucolipin 1) using a CALM (calmodulin)-dependent mechanism
Abstract
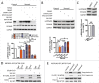
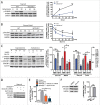
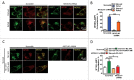
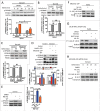
Macroautophagy/autophagy is an evolutionarily conserved pathway that is required for cellular homeostasis, growth and survival. The lysosome plays an essential role in autophagy regulation. For example, the activity of MTORC1, a master regulator of autophagy, is regulated by nutrients within the lysosome. Starvation inhibits MTORC1 causing autophagy induction. Given that MTORC1 is critical for protein synthesis and cellular homeostasis, a feedback regulatory mechanism must exist to restore MTORC1 during starvation. However, the molecular mechanism underlying this feedback regulation is unclear. In this study, we report that starvation activates the lysosomal Ca2+ release channel MCOLN1 (mucolipin 1) by relieving MTORC1's inhibition of the channel. Activated MCOLN1 in turn facilitates MTORC1 activity that requires CALM (calmodulin). Moreover, both MCOLN1 and CALM are necessary for MTORC1 reactivation during prolonged starvation. Our data suggest that lysosomal Ca2+ signaling is an essential component of the canonical MTORC1-dependent autophagy pathway and MCOLN1 provides a negative feedback regulation of MTORC1 to prevent excessive loss of MTORC1 function during starvation. The feedback regulation may be important for maintaining cellular homeostasis during starvation, as well as many other stressful or disease conditions.
Keywords: MCOLN1/mucolipin-1; MTORC1; autophagy; lysosome; lysosome Ca2+.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiency inhibits lysosomal hydrolysis.Autophagy. 2019 Sep;15(9):1572-1591. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1586256. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Autophagy. 2019. PMID: 30917721 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosomal Ca2+ release channel TRPML1 regulates lysosome size by promoting mTORC1 activity.Eur J Cell Biol. 2019 Jun;98(2-4):116-123. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2019.05.001. Epub 2019 May 14. Eur J Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31122790
-
Regulation of mTORC1 by lysosomal calcium and calmodulin.Elife. 2016 Oct 27;5:e19360. doi: 10.7554/eLife.19360. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27787197 Free PMC article.
-
MCOLN1/TRPML1 in the lysosome: a promising target for autophagy modulation in diverse diseases.Autophagy. 2024 Aug;20(8):1712-1722. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2024.2333715. Epub 2024 Mar 24. Autophagy. 2024. PMID: 38522082 Review.
-
mTORC1 and Nutrient Homeostasis: The Central Role of the Lysosome.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 12;19(3):818. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030818. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29534520 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lysosomal Calcium Channels in Autophagy and Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 15;13(6):1299. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061299. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lysosomal Potassium Channels.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2023;278:127-152. doi: 10.1007/164_2022_600. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 35879576 Review.
-
Inherited disorders of lysosomal membrane transporters.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020 Dec 1;1862(12):183336. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2020.183336. Epub 2020 May 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 32389669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insights into the Regulation of mTOR Signaling via Ca2+-Binding Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 15;24(4):3923. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043923. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted inhibition of glutamine metabolism enhances the antitumor effect of selumetinib in KRAS-mutant NSCLC.Transl Oncol. 2021 Jan;14(1):100920. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100920. Epub 2020 Nov 1. Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33137541 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
