Synergistic anticancer effects of ruxolitinib and calcitriol in estrogen receptor‑positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2‑positive breast cancer cells
- PMID: 29436642
- PMCID: PMC5865997
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8580
Synergistic anticancer effects of ruxolitinib and calcitriol in estrogen receptor‑positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2‑positive breast cancer cells
Abstract
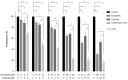
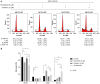
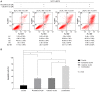
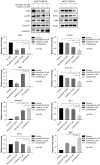
The Janus kinase (JAK)1 and JAK2 inhibitor, ruxolitinib, and the active form of vitamin D (calcitriol) were previously reported to possess anticancer effects in breast cancer. The present study investigated the combined effects of ruxolitinib and calcitriol on an estrogen receptor (ER)‑positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)‑positive, breast cancer cell line. The ER and HER2‑positive MCF7‑HER18 breast cancer cell line was used to investigate the combination effect of ruxolitinib and calcitriol. A bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) assay was used to investigate cell growth inhibition. The synergism of this combination therapy was examined using the Chou‑Talalay method. Cell cycle analysis was performed by flow cytometry, and apoptosis was evaluated by flow cytometry following Annexin V‑fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) and propidium iodide (PI) staining. Alterations in protein expression levels were analyzed by western blotting. The BrdU assay indicated that combination treatment using ruxolitinib and calcitriol produced a synergistic anti‑proliferative effect in MCF7‑HER18 breast cancer cells. Annexin V‑FITC/PI staining and cell cycle analysis identified a synergistic increase in apoptosis and sub‑G1 arrest in the presence of ruxolitinib and calcitriol. Western blot analysis revealed that these synergistic effects of ruxolitinib and calcitriol were associated with reduced protein levels of JAK2, phosphorylated JAK2, c‑Myc proto oncogene protein, cyclin‑D1, apoptosis regulator Bcl‑2 and Bcl‑2‑like protein 1, and with increased levels of caspase‑3 and Bcl‑2‑associated agonist of cell death proteins. The results of the present study demonstrated the synergistic anticancer effects of ruxolitinib and calcitriol in ER and HER2‑positive MCF7‑HER18 breast cancer cells. Based on these findings, ruxolitinib and calcitriol may have potential as a combination therapy for patients with ER and HER2‑positive breast cancer.
Keywords: breast neoplasm; ruxolitinib; calcitriol; synergism; apoptosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combinations of Calcitriol with Anticancer Treatments for Breast Cancer: An Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 25;22(23):12741. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312741. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcitriol and its analogues enhance the antiproliferative activity of gefitinib in breast cancer cells.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Apr;148:122-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.12.006. Epub 2014 Dec 12. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25510900
-
The PIM inhibitor AZD1208 synergizes with ruxolitinib to induce apoptosis of ruxolitinib sensitive and resistant JAK2-V617F-driven cells and inhibit colony formation of primary MPN cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 24;6(37):40141-57. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5653. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26472029 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Ruxolitinib and Calcitriol Combination Treatment on Various Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 25;23(5):2535. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052535. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269680 Free PMC article.
-
The potential therapeutic benefits of vitamin D in the treatment of estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.Steroids. 2012 Sep;77(11):1107-12. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2012.06.005. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Steroids. 2012. PMID: 22801352 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin D and potential effects on cancers: a review.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Jan 25;51(1):190. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09111-y. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38270702 Review.
-
Combinations of Calcitriol with Anticancer Treatments for Breast Cancer: An Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 25;22(23):12741. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312741. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Visible Light-Promoted Green and Sustainable Approach for One-Pot Synthesis of 4,4'-(Arylmethylene)bis(1H-pyrazol-5-ols), In Vitro Anticancer Activity, and Molecular Docking with Covid-19 Mpro.ACS Omega. 2022 Sep 14;7(38):34583-34598. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04506. eCollection 2022 Sep 27. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36188265 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of tumor growth and angiogenesis of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells by ruxolitinib, a selective JAK2 inhibitor.Oncol Lett. 2019 Apr;17(4):3981-3989. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10059. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30930994 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects of p-methoxycinnamic acid, an active phenylpropanoid, against 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced rat colon carcinogenesis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 Jan;451(1-2):117-129. doi: 10.1007/s11010-018-3398-5. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 29980883
References
-
- Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thürlimann B, Senn HJ, Panel members Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: Highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2013. Ann Oncol. 2013;24:2206–2223. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt303. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

