The Neurotropic Properties of AAV-PHP.B Are Limited to C57BL/6J Mice
- PMID: 29428298
- PMCID: PMC5911151
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.01.018
The Neurotropic Properties of AAV-PHP.B Are Limited to C57BL/6J Mice
Abstract
Improved delivery of adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors to the CNS will greatly enhance their clinical utility. Selection of AAV9 variants in a mouse model led to the isolation of a capsid called PHP.B, which resulted in remarkable transduction of the CNS following intravenous infusion. However, we now show here that this enhanced CNS tropism is restricted to the model in which it was selected, i.e., a Cre transgenic mouse in a C57BL/6J background, and was not found in nonhuman primates or the other commonly used mouse strain BALB/cJ. We also report the potential for serious acute toxicity in NHP after systemic administration of high dose of AAV.
Copyright © 2018 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
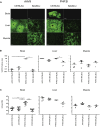
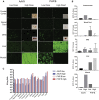
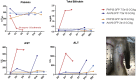
Comment in
-
Safety First: Perspective on Patient-Centered Development of AAV Gene Therapy Products.Mol Ther. 2018 Mar 7;26(3):669-671. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.02.009. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Mol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29503193 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Context-Specific Function of the Engineered Peptide Domain of PHP.B.J Virol. 2021 Sep 27;95(20):e0116421. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01164-21. Epub 2021 Aug 4. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34346767 Free PMC article.
-
Ly6a Differential Expression in Blood-Brain Barrier Is Responsible for Strain Specific Central Nervous System Transduction Profile of AAV-PHP.B.Hum Gene Ther. 2020 Jan;31(1-2):90-102. doi: 10.1089/hum.2019.186. Epub 2019 Dec 13. Hum Gene Ther. 2020. PMID: 31696742
-
AAV-PHP.B Administration Results in a Differential Pattern of CNS Biodistribution in Non-human Primates Compared with Mice.Mol Ther. 2019 Nov 6;27(11):2018-2037. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.07.017. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Mol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31420242 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor targeting of adeno-associated virus vectors.Gene Ther. 2003 Jul;10(14):1142-51. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3301976. Gene Ther. 2003. PMID: 12833123 Review.
-
Gene therapy for the CNS using AAVs: The impact of systemic delivery by AAV9.J Control Release. 2016 Nov 10;241:94-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.09.011. Epub 2016 Sep 13. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 27637390 Review.
Cited by
-
Towards the Clinical Application of Gene Therapy for Genetic Inner Ear Diseases.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 29;12(3):1046. doi: 10.3390/jcm12031046. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36769694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intravenous functional gene transfer throughout the brain of non-human primates using AAV.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 13:rs.3.rs-1370972. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-1370972/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Nat Nanotechnol. 2023 Oct;18(10):1241-1251. doi: 10.1038/s41565-023-01419-x. PMID: 36789432 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Brain-wide TVA compensation allows rabies virus to retrograde target cell-type-specific projection neurons.Mol Brain. 2022 Jan 29;15(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13041-022-00898-8. Mol Brain. 2022. PMID: 35093138 Free PMC article.
-
Current Landscape of Heart Failure Gene Therapy.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 May 21;8(10):e012239. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012239. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31070089 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Context-Specific Function of the Engineered Peptide Domain of PHP.B.J Virol. 2021 Sep 27;95(20):e0116421. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01164-21. Epub 2021 Aug 4. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34346767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gao G., Vandenberghe L.H., Wilson J.M. New recombinant serotypes of AAV vectors. Curr. Gene Ther. 2005;5:285–297. - PubMed
-
- Pacak C.A., Mah C.S., Thattaliyath B.D., Conlon T.J., Lewis M.A., Cloutier D.E., Zolotukhin I., Tarantal A.F., Byrne B.J. Recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 9 leads to preferential cardiac transduction in vivo. Circ. Res. 2006;99:e3–e9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

