Maternal IgG immune complexes induce food allergen-specific tolerance in offspring
- PMID: 29158374
- PMCID: PMC5748859
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20171163
Maternal IgG immune complexes induce food allergen-specific tolerance in offspring
Abstract
The role of maternal immune responses in tolerance induction is poorly understood. To study whether maternal allergen sensitization affects offspring susceptibility to food allergy, we epicutaneously sensitized female mice with ovalbumin (OVA) followed by epicutaneous sensitization and oral challenge of their offspring with OVA. Maternal OVA sensitization prevented food anaphylaxis, OVA-specific IgE production, and intestinal mast cell expansion in offspring. This protection was mediated by neonatal crystallizable fragment receptor (FcRn)-dependent transfer of maternal IgG and OVA immune complexes (IgG-IC) via breast milk and induction of allergen-specific regulatory T (T reg) cells in offspring. Breastfeeding by OVA-sensitized mothers or maternal supplementation with IgG-IC was sufficient to induce neonatal tolerance. FcRn-dependent antigen presentation by CD11c+ dendritic cells (DCs) in offspring was required for oral tolerance. Human breast milk containing OVA-IgG-IC induced tolerance in humanized FcRn mice. Collectively, we demonstrate that interactions of maternal IgG-IC and offspring FcRn are critical for induction of T reg cell responses and control of food-specific tolerance in neonates.
© 2018 Ohsaki et al.
Figures
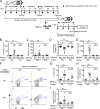




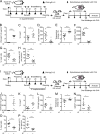


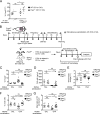

Comment in
-
FcRn is mother's milk to allergen tolerance.J Exp Med. 2018 Jan 2;215(1):1-3. doi: 10.1084/jem.20172022. Epub 2017 Dec 1. J Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 29196507 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
IgG Expression upon Oral Sensitization in Association with Maternal Exposure to Ovalbumin.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 4;11(2):e0148251. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148251. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26844775 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal immunization with ovalbumin prevents neonatal allergy development and up-regulates inhibitory receptor Fc gamma RIIB expression on B cells.BMC Immunol. 2010 Mar 11;11:11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-11-11. BMC Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20222978 Free PMC article.
-
Immune suppression of food allergy by maternal IgG in murine models.Allergol Int. 2018 Oct;67(4):506-514. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2018.04.001. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Allergol Int. 2018. PMID: 29724483
-
The Neonatal Fc Receptor (FcRn): A Misnomer?Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 10;10:1540. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01540. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31354709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influences of Maternal Factors Over Offspring Allergies and the Application for Food Allergy.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 23;10:1933. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01933. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31507589 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oral tolerance to dietary antigens and Foxp3+ regulatory T cells.Immunol Rev. 2024 Sep;326(1):8-16. doi: 10.1111/imr.13370. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Immunol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39054615 Review.
-
The right educational environment: Oral tolerance in early life.Immunol Rev. 2024 Sep;326(1):17-34. doi: 10.1111/imr.13366. Epub 2024 Jul 13. Immunol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39001685 Review.
-
IgG and IgM responses to the Plasmodium falciparum asexual stage antigens reflect respectively protection against malaria during pregnancy and infanthood.Malar J. 2024 May 19;23(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12936-024-04970-7. Malar J. 2024. PMID: 38764069 Free PMC article.
-
IgG exacerbates genital chlamydial pathology in females by enhancing pathogenic CD8+ T cell responses.Scand J Immunol. 2024 Jan;99(1):e13331. doi: 10.1111/sji.13331. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Scand J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38441219 Free PMC article.
-
IgG in the control of FcεRI activation: a battle on multiple fronts.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 11;14:1339171. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1339171. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38274816 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bai Y., Ye L., Tesar D.B., Song H., Zhao D., Björkman P.J., Roopenian D.C., and Zhu X.. 2011. Intracellular neutralization of viral infection in polarized epithelial cells by neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn)-mediated IgG transport. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 108:18406–18411. 10.1073/pnas.1115348108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker K., Qiao S.W., Kuo T.T., Aveson V.G., Platzer B., Andersen J.T., Sandlie I., Chen Z., de Haar C., Lencer W.I., et al. . 2011. Neonatal Fc receptor for IgG (FcRn) regulates cross-presentation of IgG immune complexes by CD8-CD11b+ dendritic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 108:9927–9932. 10.1073/pnas.1019037108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

