The mTORC1 Signaling Network Senses Changes in Cellular Purine Nucleotide Levels
- PMID: 29091770
- PMCID: PMC5689476
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.029
The mTORC1 Signaling Network Senses Changes in Cellular Purine Nucleotide Levels
Abstract
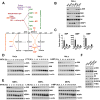
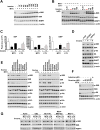
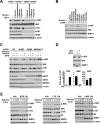
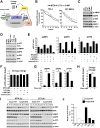
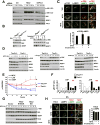
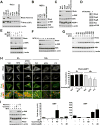
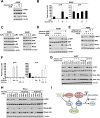
Mechanistic (or mammalian) target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) integrates signals from growth factors and nutrients to control biosynthetic processes, including protein, lipid, and nucleic acid synthesis. We find that the mTORC1 pathway is responsive to changes in purine nucleotides in a manner analogous to its sensing of amino acids. Depletion of cellular purines, but not pyrimidines, inhibits mTORC1, and restoration of intracellular adenine nucleotides via addition of exogenous purine nucleobases or nucleosides acutely reactivates mTORC1. Adenylate sensing by mTORC1 is dependent on the tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) protein complex and its regulation of Rheb upstream of mTORC1, but independent of energy stress and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Even though mTORC1 signaling is not acutely sensitive to changes in intracellular guanylates, long-term depletion of guanylates decreases Rheb protein levels. Our findings suggest that nucleotide sensing, like amino acid sensing, enables mTORC1 to tightly coordinate nutrient availability with the synthesis of macromolecules, such as protein and nucleic acids, produced from those nutrients.
Keywords: AMPK; ATP; GTP; Rag GTPases; Rheb; mTOR; nucleotides; nutrient sensing; purine; tuberous sclerosis complex.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Purine Nucleotide Availability Regulates mTORC1 Activity through the Rheb GTPase.Cell Rep. 2017 Jun 27;19(13):2665-2680. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.043. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28658616
-
mTORC1 Couples Nucleotide Synthesis to Nucleotide Demand Resulting in a Targetable Metabolic Vulnerability.Cancer Cell. 2017 Nov 13;32(5):624-638.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.09.013. Epub 2017 Oct 19. Cancer Cell. 2017. PMID: 29056426 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamine and asparagine activate mTORC1 independently of Rag GTPases.J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 6;295(10):2890-2899. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AC119.011578. Epub 2020 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32019866 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acid-dependent control of mTORC1 signaling: a variety of regulatory modes.J Biomed Sci. 2020 Aug 17;27(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12929-020-00679-2. J Biomed Sci. 2020. PMID: 32799865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of mTORC1 by PI3K signaling.Trends Cell Biol. 2015 Sep;25(9):545-55. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.06.002. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Trends Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26159692 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Purinosomes and Purine Metabolism in Mammalian Neural Development: A Review.Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2024 Jun 28;57(3):89-100. doi: 10.1267/ahc.24-00027. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2024. PMID: 38988694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DN200434 Inhibits Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Prevents Neointima Formation in Mice after Carotid Artery Ligation.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2022 Oct;37(5):800-809. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2022.1462. Epub 2022 Sep 28. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2022. PMID: 36168774 Free PMC article.
-
Lipidomics and Transcriptomics Differ Liposarcoma Differentiation Characteristics That Can Be Altered by Pentose Phosphate Pathway Intervention.Metabolites. 2022 Dec 7;12(12):1227. doi: 10.3390/metabo12121227. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36557266 Free PMC article.
-
Pathway-specific effects of ADSL deficiency on neurodevelopment.Elife. 2022 Feb 8;11:e70518. doi: 10.7554/eLife.70518. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35133277 Free PMC article.
-
T cell activation triggers reversible inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase assembly.J Cell Sci. 2018 Sep 5;131(17):jcs223289. doi: 10.1242/jcs.223289. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 30154209 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chabner BA, Roberts TG., Jr Timeline: Chemotherapy and the war on cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:65–72. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

