Apolipoprotein E4 Impairs Neuronal Insulin Signaling by Trapping Insulin Receptor in the Endosomes
- PMID: 28957663
- PMCID: PMC5621659
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.09.003
Apolipoprotein E4 Impairs Neuronal Insulin Signaling by Trapping Insulin Receptor in the Endosomes
Abstract
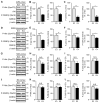
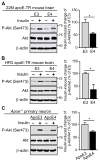
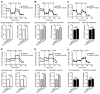
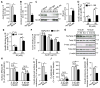
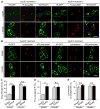
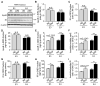
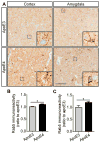
Diabetes and impaired brain insulin signaling are linked to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The association between diabetes and AD-associated amyloid pathology is stronger among carriers of the apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 gene allele, the strongest genetic risk factor for late-onset AD. Here we report that apoE4 impairs neuronal insulin signaling in human apoE-targeted replacement (TR) mice in an age-dependent manner. High-fat diet (HFD) accelerates these effects in apoE4-TR mice at middle age. In primary neurons, apoE4 interacts with insulin receptor and impairs its trafficking by trapping it in the endosomes, leading to impaired insulin signaling and insulin-stimulated mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis. In aging brains, the increased apoE4 aggregation and compromised endosomal function further exacerbate the inhibitory effects of apoE4 on insulin signaling and related functions. Together, our study provides novel mechanistic insights into the pathogenic mechanisms of apoE4 and insulin resistance in AD.
Keywords: APOE; Aggregation; Aging; Alzheimer’s disease; Endosomal dysfunction; Insulin signaling; Trafficking.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Central and Peripheral Mechanisms in ApoE4-Driven Diabetic Pathology.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 14;21(4):1289. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041289. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32075060 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Signaling Mediated by ApoE2, ApoE3, and ApoE4 in Human Neurons Parallels Alzheimer's Disease Risk.J Neurosci. 2019 Sep 11;39(37):7408-7427. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2994-18.2019. Epub 2019 Jul 22. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31331998 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E2 Expression Alters Endosomal Pathways in a Mouse Model With Increased Brain Exosome Levels During Aging.Traffic. 2024 May;25(5):e12937. doi: 10.1111/tra.12937. Traffic. 2024. PMID: 38777335
-
Apolipoprotein E isoforms in Alzheimer's disease pathology and etiology.Microsc Res Tech. 2000 Aug 15;50(4):278-81. doi: 10.1002/1097-0029(20000815)50:4<278::AID-JEMT5>3.0.CO;2-T. Microsc Res Tech. 2000. PMID: 10936880 Review.
-
Apolipoprotein E and oxidative stress in brain with relevance to Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 May;138:104795. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104795. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32036033 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular landscape of the overlap between Alzheimer's disease and somatic insulin-related diseases.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 Oct 28;16(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01609-2. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39465382 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Impaired Receptor Trafficking in Mediating the Pathological Effects of APOE4 in Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2024;97(2):753-775. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230514. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 38217595 Free PMC article.
-
β-Hydroxybutyrate inhibits inflammasome activation to attenuate Alzheimer's disease pathology.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Sep 21;17(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01948-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32958021 Free PMC article.
-
Brain integrity is altered by hepatic APOE ε4 in humanized-liver mice.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Aug;27(8):3533-3543. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01548-0. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35418601 Free PMC article.
-
TRPV1 regulates ApoE4-disrupted intracellular lipid homeostasis and decreases synaptic phagocytosis by microglia.Exp Mol Med. 2023 Feb;55(2):347-363. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-00935-z. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Exp Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36720919 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aleshkov S, Abraham CR, Zannis VI. Interaction of nascent ApoE2, ApoE3, and ApoE4 isoforms expressed in mammalian cells with amyloid peptide beta (1–40). Relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. Biochemistry. 1997;36:10571–10580. - PubMed
-
- Anthopoulos PG, Hamodrakas SJ, Bagos PG. Apolipoprotein E polymorphisms and type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of 30 studies including 5423 cases and 8197 controls. Mol Genet Metab. 2010;100:283–291. - PubMed
-
- Beitner R, Kalant N. Stimulation of glycolysis by insulin. J Biol Chem. 1971;246:500–503. - PubMed
-
- Biessels GJ, Staekenborg S, Brunner E, Brayne C, Scheltens P. Risk of dementia in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:64–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

