Hsp90 activator Aha1 drives production of pathological tau aggregates
- PMID: 28827321
- PMCID: PMC5594679
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1707039114
Hsp90 activator Aha1 drives production of pathological tau aggregates
Abstract
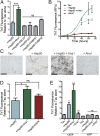
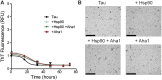
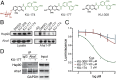
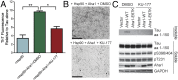
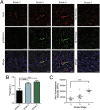
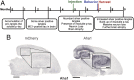
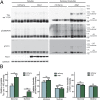
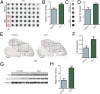
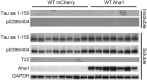
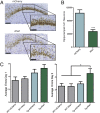
The microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT, tau) forms neurotoxic aggregates that promote cognitive deficits in tauopathies, the most common of which is Alzheimer's disease (AD). The 90-kDa heat shock protein (Hsp90) chaperone system affects the accumulation of these toxic tau species, which can be modulated with Hsp90 inhibitors. However, many Hsp90 inhibitors are not blood-brain barrier-permeable, and several present associated toxicities. Here, we find that the cochaperone, activator of Hsp90 ATPase homolog 1 (Aha1), dramatically increased the production of aggregated tau. Treatment with an Aha1 inhibitor, KU-177, dramatically reduced the accumulation of insoluble tau. Aha1 colocalized with tau pathology in human brain tissue, and this association positively correlated with AD progression. Aha1 overexpression in the rTg4510 tau transgenic mouse model promoted insoluble and oligomeric tau accumulation leading to a physiological deficit in cognitive function. Overall, these data demonstrate that Aha1 contributes to tau fibril formation and neurotoxicity through Hsp90. This suggests that therapeutics targeting Aha1 may reduce toxic tau oligomers and slow or prevent neurodegenerative disease progression.
Keywords: Aha1; Alzheimer’s disease; Hsp90; chaperones; tau oligomers.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: C.A.D., L.B.S., B.S.J.B., J.K., and L.J.B. are the coinventors for the following provisional patent application: “The Hsp90 Activator Aha1 Drives Production of Pathological Tau Aggregates.”
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hsp90 co-chaperones, FKBP52 and Aha1, promote tau pathogenesis in aged wild-type mice.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021 Apr 8;9(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s40478-021-01159-w. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021. PMID: 33832539 Free PMC article.
-
The high-affinity HSP90-CHIP complex recognizes and selectively degrades phosphorylated tau client proteins.J Clin Invest. 2007 Mar;117(3):648-58. doi: 10.1172/JCI29715. Epub 2007 Feb 15. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17304350 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp90 regulates tau pathology through co-chaperone complexes in Alzheimer's disease.Prog Neurobiol. 2011 Jan;93(1):99-110. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.10.006. Epub 2010 Nov 5. Prog Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21056617 Review.
-
Hsp90 Oligomers Interacting with the Aha1 Cochaperone: An Outlook for the Hsp90 Chaperone Machineries.Anal Chem. 2015 Jul 21;87(14):7043-51. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00051. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 26076190
-
Imbalances in the Hsp90 Chaperone Machinery: Implications for Tauopathies.Front Neurosci. 2017 Dec 22;11:724. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00724. eCollection 2017. Front Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29311797 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
FKBP52 overexpression accelerates hippocampal-dependent memory impairments in a tau transgenic mouse model.NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2021 May 3;7(1):9. doi: 10.1038/s41514-021-00062-x. NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2021. PMID: 33941782 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional complexity of HSP90 in cellular homeostasis and disease.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Nov;24(11):797-815. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00640-9. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37524848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HSP27 Modulates Neuropathic Pain by Inhibiting P2X3 Degradation.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Feb;61(2):707-724. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03582-7. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37656312
-
Targeting the FKBP51/GR/Hsp90 Complex to Identify Functionally Relevant Treatments for Depression and PTSD.ACS Chem Biol. 2018 Aug 17;13(8):2288-2299. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.8b00454. Epub 2018 Jun 19. ACS Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29893552 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Hsp90 mechanism and in vivo functions learned from studies in the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Feb 8;11:1325590. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1325590. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38389899 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee VM, Goedert M, Trojanowski JQ. Neurodegenerative tauopathies. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:1121–1159. - PubMed
-
- Ballatore C, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ. Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:663–672. - PubMed
-
- Caughey B, Lansbury PT. Protofibrils, pores, fibrils, and neurodegeneration: Separating the responsible protein aggregates from the innocent bystanders. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2003;26:267–298. - PubMed
-
- Sahara N, et al. Molecular chaperone-mediated tau protein metabolism counteracts the formation of granular tau oligomers in human brain. J Neurosci Res. 2007;85:3098–3108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

