An Epstein-Barr Virus MicroRNA Blocks Interleukin-1 (IL-1) Signaling by Targeting IL-1 Receptor 1
- PMID: 28794034
- PMCID: PMC5640834
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00530-17
An Epstein-Barr Virus MicroRNA Blocks Interleukin-1 (IL-1) Signaling by Targeting IL-1 Receptor 1
Abstract
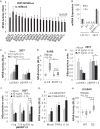
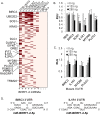
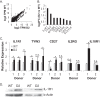
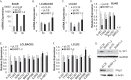
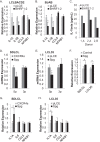
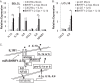
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) encodes >44 viral microRNAs (miRNAs) that are differentially expressed throughout infection, can be detected in Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive tumors, and manipulate several biological processes, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, and immune responses. Here, we show that EBV BHRF1-2 miRNAs block NF-κB activation following treatment with proinflammatory cytokines, specifically interleukin-1β (IL-1β). Analysis of EBV PAR-CLIP miRNA targetome data sets combined with pathway analysis revealed multiple BHRF1-2 miRNA targets involved in interleukin signaling pathways. By further analyzing changes in cellular gene expression patterns, we identified the IL-1 receptor 1 (IL1R1) as a direct target of miR-BHRF1-2-5p. Targeting the IL1R1 3' untranslated region (UTR) by EBV miR-BHRF1-2-5p was confirmed using 3'-UTR luciferase reporter assays and Western blot assays. Manipulation of EBV BHRF1-2 miRNA activity in latently infected B cells altered steady-state cytokine levels and disrupted IL-1β responsiveness. These studies demonstrate functionally relevant BHRF1-2 miRNA interactions during EBV infection, which is an important step in understanding their roles in pathogenesis.IMPORTANCE IL-1 signaling plays an important role in inflammation and early activation of host innate immune responses following virus infection. Here, we demonstrate that a viral miRNA downregulates the IL-1 receptor 1 during EBV infection, which consequently alters the responsiveness of cells to IL-1 stimuli and changes the cytokine expression levels within infected cell populations. We postulate that this viral miRNA activity not only disrupts IL-1 autocrine and paracrine signaling loops that can alert effector cells to sites of infection but also provides a survival advantage by dampening excessive inflammation that may be detrimental to the infected cell.
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus; RNA interference; cytokines; herpesviruses; interleukins; microRNA.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
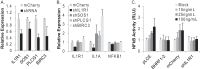
Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs regulate B cell receptor signal transduction and lytic reactivation.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Jan 7;15(1):e1007535. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007535. eCollection 2019 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30615681 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus miR-BHRF1-3 Targets the BZLF1 3'UTR and Regulates the Lytic Cycle.J Virol. 2022 Feb 23;96(4):e0149521. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01495-21. Epub 2021 Dec 8. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34878852 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA miR-BART20-5p stabilizes Epstein-Barr virus latency by directly targeting BZLF1 and BRLF1.J Virol. 2014 Aug;88(16):9027-37. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00721-14. Epub 2014 Jun 4. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24899173 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs.Semin Cancer Biol. 2014 Jun;26:52-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.02.002. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014. PMID: 24602823 Review.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
EBV-microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in EBV-related Fever: A Narrative Review.Curr Mol Med. 2024;24(1):2-13. doi: 10.2174/1566524023666221118122005. Curr Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 36411555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implication of viral microRNAs in the genesis and diagnosis of Epstein-Barr virus-associated tumors.Oncol Lett. 2019 Oct;18(4):3433-3442. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10713. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31516561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Emerging Role of Non-Coding RNAs in the Regulation of Virus Replication and Resultant Cellular Pathologies.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 13;23(2):815. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020815. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35055001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs regulate B cell receptor signal transduction and lytic reactivation.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Jan 7;15(1):e1007535. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007535. eCollection 2019 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30615681 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs: EBV Mechanism for Escaping Host's Immune Response and Supporting Tumorigenesis.Pathogens. 2020 May 8;9(5):353. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9050353. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32397085 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

