Bushehr Elderly Health (BEH) programme: study protocol and design of musculoskeletal system and cognitive function (stage II)
- PMID: 28780537
- PMCID: PMC5577871
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013606
Bushehr Elderly Health (BEH) programme: study protocol and design of musculoskeletal system and cognitive function (stage II)
Abstract
Introduction: Musculoskeletal disorders and cognitive diseases are prevalent, and they are significant determinants of morbidity and mortality in older adults. The aim of this study is to investigate the prevalence of musculoskeletal and cognitive diseases and their risk factors and also to assess their associations during future follow-ups.
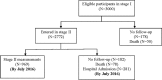
Methods and analysis: Bushehr Elderly Health (BEH) programme is a population-based prospective cohort study being conducted in Bushehr, a southern province of Iran. A total of 3000 older people aged ≥60 years participated in the first stage from which 2772 were eligible to participate in the second stage, which started after 2.5 years. Data including demographic status, lifestyle factors, general healthandmedical history, and mentalandfunctional health are collected through a questionnaire. Anthropometric measures, performance testsandmuscle strength, blood pressure and and body composition measurements are done. A total 25 cc venous blood is taken, and sera are stored at -80°C for possible future analyses.
Ethics and dissemination: The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of Endocrinology and Metabolism Research Institute, affiliated to Tehran University of Medical Science as well as the Research Ethics Committee of Bushehr University of Medical Sciences. A written informed consent was signed by all the participants. The study findings will show the prevalence of musculoskeletal disease, cognitive impairment and their risk factors in an elderly population. The participants will be followed during the study to measure the occurrence outcomes.This study will also have the potential to inform the development of beneficial interventions to improve the management of musculoskeletal and cognitive impairment in Iran and other countries in the Middle East.Our findings will be disseminated via scientific publication as well as presentation to stakeholders, including the patients, clinicians, the public and policymakers, via appropriate avenues.
Keywords: cognitive function; elderly; musculoskeletal system; protocol.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2017. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bushehr Elderly Health (BEH) Programme, phase I (cardiovascular system).BMJ Open. 2015 Dec 16;5(12):e009597. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-009597. BMJ Open. 2015. PMID: 26674503 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Analysing cardiovascular risk factors and related outcomes in a middle-aged to older adults population in Iran: a cohort protocol of the Shiraz Heart Study (SHS).BMJ Open. 2019 Apr 3;9(4):e026317. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-026317. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 30948600 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoporosis and cognitive impairment interwoven warning signs: community-based study on older adults-Bushehr Elderly Health (BEH) Program.Arch Osteoporos. 2020 Sep 10;15(1):140. doi: 10.1007/s11657-020-00817-1. Arch Osteoporos. 2020. PMID: 32910343
-
Prevalence of chronic musculoskeletal disorders in elderly Brazilians: a systematic review of the literature.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012 May 29;13:82. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-13-82. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012. PMID: 22642899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Musculoskeletal Deficits and Cognitive Impairment: Epidemiological Evidence and Biological Mechanisms.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2022 Oct;20(5):260-272. doi: 10.1007/s11914-022-00736-9. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2022. PMID: 35764750 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sarcopenia disease in Iran: an overview.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2019 Nov 15;18(2):665-674. doi: 10.1007/s40200-019-00452-9. eCollection 2019 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2019. PMID: 31890691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of osteoporosis among the elderly population of Iran.Arch Osteoporos. 2021 Jan 21;16(1):16. doi: 10.1007/s11657-020-00872-8. Arch Osteoporos. 2021. PMID: 33475880
-
Identifying determinants for falls among Iranian older adults: insights from the Bushehr Elderly Health Program.BMC Geriatr. 2024 Jul 9;24(1):588. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05180-1. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 38982344 Free PMC article.
-
Association between biomarkers of bone health and osteosarcopenia among Iranian older people: The Bushehr Elderly Health (BEH) program.BMC Geriatr. 2021 Nov 19;21(1):654. doi: 10.1186/s12877-021-02608-w. BMC Geriatr. 2021. PMID: 34798818 Free PMC article.
-
Grand multiparity associations with low bone mineral density and degraded trabecular bone pattern.Bone Rep. 2021 Apr 22;14:101071. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2021.101071. eCollection 2021 Jun. Bone Rep. 2021. PMID: 33997148 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Interesting facts about ageing. secondary interesting facts about ageing. 2012. http://www.who.int/ageing/about/facts/en/index.html.
-
- Public relations and International Cooperation. Selected Findings of National Population and Housing Census, 2012. Tehran: Statistical Center of Iran, 2011:27.
-
- Larijani B, Bonjour JP, Resch H, et al. . Osteoporosis in Iran, Overview and Management. Iranian J Publ Health 2007(supp 1):1–13.
-
- Kanis JA. Assessment of Osteoporosis at the Primary Health Care Level WHO Technical Report Series. 66 UK: University of Sheffield, 2007.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical