Gellified Emulsion of Ofloxacin for Transdermal Drug Delivery System
- PMID: 28761825
- PMCID: PMC5527237
- DOI: 10.15171/apb.2017.028
Gellified Emulsion of Ofloxacin for Transdermal Drug Delivery System
Abstract
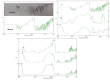
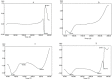
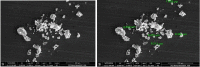
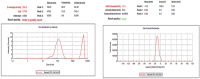
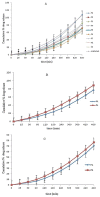
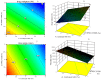
Purpose: Ofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone with broad-spectrum antibacterial action, used in treatment of systemic and local infections. Ofloxacin is BCS class II drug having low solubility, high permeability with short half-life. The present work was aimed to design, develop and optimize gellified emulsion of Ofloxacin to provide site targeted drug delivery. Transdermal drug delivery will enhance the bioavailability of the drug giving controlled drug release. Methods: Transdermal drug delivery system was designed with gelling agent (Carbopol 940 and HPMC K100M), oil phase (oleic acid) and emulsifying agent (Tween 80: Span 80). Effect of concentration of gelling agent on release of drug from transdermal delivery was studied by 32 factorial design. Emulgel was evaluated for physical appearance, pH, drug content, viscosity, spreadability, antimicrobial activity, in- vitro diffusion study and ex-vivo diffusion study. Results: FE-SEM study of the emulsion batch B5 has revealed formation of emulsion globules of approximately size 6-8 µm with -11.2 mV zeta potential showing good stability for the emulsion. Carbopol 940 had shown greater linear effect on drug release and viscosity of the formulations due to its high degree of gelling. In-vitro diffusion study through egg membrane had shown 88.58±1.82 % drug release for optimized batch F4. Ex-vivo diffusion study through goat skin indicated 76.68 ± 2.52% drug release. Conclusion: Controlled release Ofloxacin emulgel exhibiting good in-vitro and ex-vivo drug release proving good antimicrobial property was formulated.
Keywords: Antimicrobial; Delivery; Emulgel; Emulsion; Ofloxacin; Transdermal.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of Microemulsion Based Nabumetone Transdermal Delivery for Treatment of Arthritis.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2018;12(2):130-149. doi: 10.2174/1872211312666180227091059. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2018. PMID: 29485013
-
Development of Emulgel Delivery of Mupirocin for Treatment of Skin Infection.Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2020;15(2):137-156. doi: 10.2174/1386207323999200819153404. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2020. PMID: 32814540
-
Formulation development, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of microemulsion-based gel loaded with ketoprofen.Drug Deliv. 2015;22(4):509-15. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2013.859186. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 24266589
-
Cellulose derivatives and natural gums as gelling agents for preparation of emulgel-based dosage forms: A brief review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jun 30;241:124538. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124538. Epub 2023 Apr 19. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37085064 Review.
-
Recent expansions in an emergent novel drug delivery technology: Emulgel.J Control Release. 2013 Oct 28;171(2):122-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.06.030. Epub 2013 Jul 2. J Control Release. 2013. PMID: 23831051 Review.
Cited by
-
Design, Formulation, and Evaluation of Aloe vera Gel-Based Capsaicin Transemulgel for Osteoarthritis.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Aug 29;14(9):1812. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14091812. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36145560 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrophobic Drug Carrier from Polycaprolactone-b-Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Star-Shaped Polymers Hydrogel Blend as Potential for Wound Healing Application.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Apr 27;15(9):2072. doi: 10.3390/polym15092072. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37177238 Free PMC article.
-
Ginger Extract-Loaded Sesame Oil-Based Niosomal Emulgel: Quality by Design to Ameliorate Anti-Inflammatory Activity.Gels. 2022 Nov 14;8(11):737. doi: 10.3390/gels8110737. Gels. 2022. PMID: 36421559 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Steam Sterilization on the Properties of Stimuli-Responsive Polymer-Based Hydrogels.Gels. 2023 May 6;9(5):385. doi: 10.3390/gels9050385. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37232977 Free PMC article.
-
Development and efficacy of tryptophol-containing emulgel for reducing subcutaneous fungal nodules from Scedosporium apiospermum eumycetoma.Res Pharm Sci. 2022 Oct 29;17(6):707-722. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.359437. eCollection 2022 Dec. Res Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 36704435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jhawat VC, Saini V, Kambooj S, Maggon N. Transdermal drug delivery systems: approaches and advancements in drug absorption through skin. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2013;20(1):47–56.
-
- Singla V, Saini S, Joshi B, Rana AC. Emulgel: A new platform for topical drug delivery. Int J Pharm Bio Sci. 2012;3(1):485–98.
-
- Government of India. Ministry of health and welfare. Indian Pharmacopoeia, Vol. I, II. New Delhi: Controller of Publications; 2014.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources