LncRNA SNHG15 contributes to proliferation, invasion and autophagy in osteosarcoma cells by sponging miR-141
- PMID: 28720111
- PMCID: PMC5516387
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-017-0353-9
LncRNA SNHG15 contributes to proliferation, invasion and autophagy in osteosarcoma cells by sponging miR-141
Abstract
Background: LncRNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 15 (SNHG15) was reported to play an oncogenic role in tumors. However, the role of SNHG15 and its molecular mechanism in osteosarcoma (OS) cells are largely unknown.
Methods: qRT-PCR was performed to evaluate the expression levels of SNHG15 and miR-141 in OS tissues and cells. Cell transfection with different siRNAs, miRNAs or pcDNAs into U2OS and MG63 cells were carried out by Lipofectamine 2000. The effects of SNHG15 and miR-141 on OS cell proliferation, invasion and the levels of autophagy-related proteins were analyzed by MTT assay, Transwell invasion/migration assay and western blot, respectively. Luciferase reporter assay was used to confirm whether SNHG15 could directly interact with miR-141.
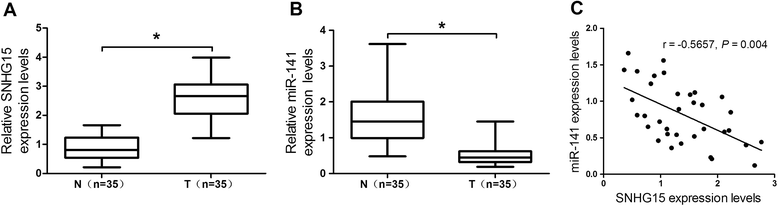
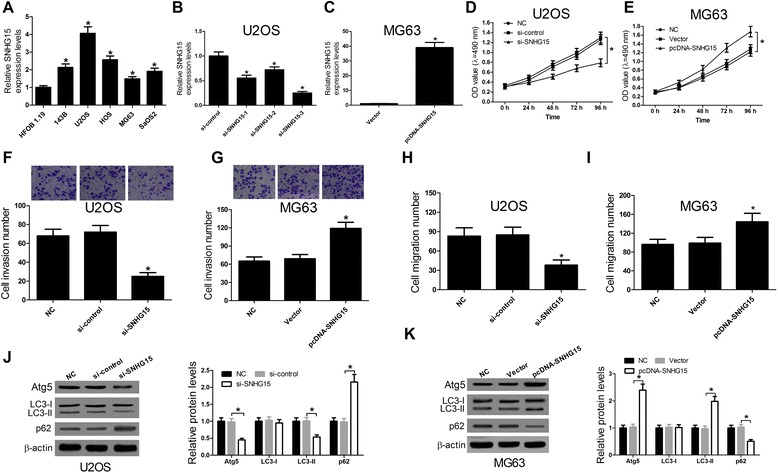
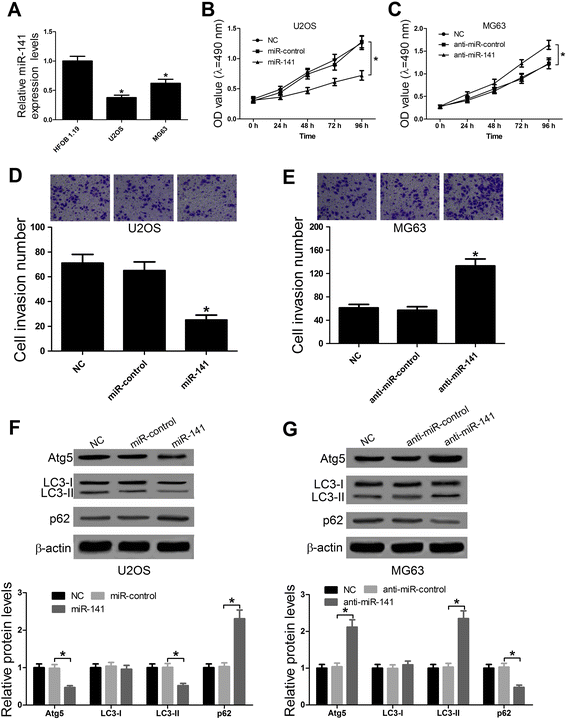
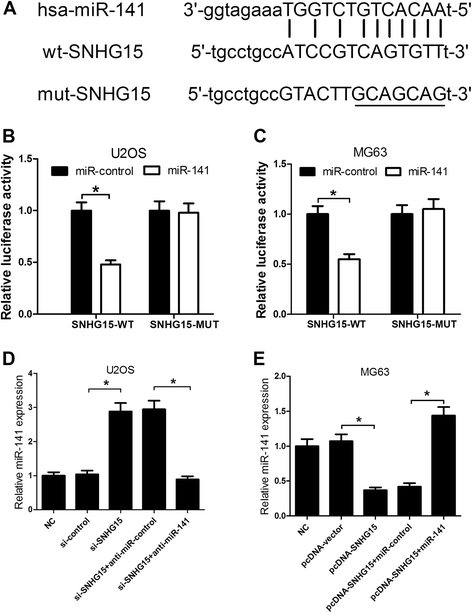
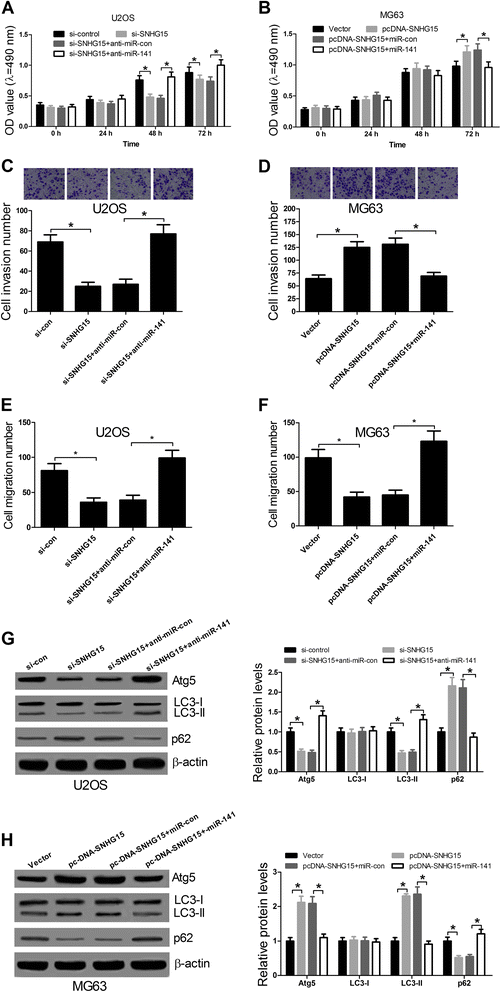
Results: We found that up-regulation of SNHG15 was inversely correlated with miR-141 expression in OS tissues. SNHG15 knockdown and miR-141 overexpression significantly suppressed cell proliferation, invasion, migration and autophagy while SNHG15 overexpression and miR-141 repression exhibited the opposite effects on OS cells. Besides, SNHG15 could directly interact with miR-141 and regulate its expression. Furthermore, miR-141 suppressing significantly overturned the inhibition on proliferation, invasion, migration and autophagy mediated by SNHG15 knockdown while miR-141 overexpression remarkably attenuated SNHG15 overexpression-induced proliferation, invasion, migration and autophagy in OS cells.
Conclusion: Our data showed that SNHG15 contributes to proliferation, invasion, migration and autophagy in OS by negatively regulating miR-141, providing a new potential target and prognostic biomarker for the treatment of OS.
Keywords: Osteosarcoma; Sponge; lncRNA SNHG15; miR-141.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
Ke Liu, the first author. Jia Zheng, the corresponding author.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors have consented for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LncRNA SNHG16 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by targeting miR-1301/BCL9 axis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jun;114:108798. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108798. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30909141
-
Long noncoding RNA SNHG15 promotes human breast cancer proliferation, migration and invasion by sponging miR-211-3p.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Jan 8;495(2):1594-1600. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.12.013. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29217194
-
LncRNA LINC00313 Knockdown Inhibits Tumorigenesis and Metastasis in Human Osteosarcoma by Upregulating FOSL2 through Sponging miR-342-3p.Yonsei Med J. 2020 May;61(5):359-370. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2020.61.5.359. Yonsei Med J. 2020. PMID: 32390359 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA SNHG15: A potential therapeutic target in the treatment of colorectal cancer.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2023 May;101(5):1138-1150. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14036. Epub 2022 Feb 27. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2023. PMID: 35191201 Review.
-
SNHG15: a promising cancer-related long noncoding RNA.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Jul 1;11:5961-5969. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S208054. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31308739 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Down-regulation LncRNA-SNHG15 contributes to proliferation and invasion of bladder cancer cells.BMC Urol. 2021 May 20;21(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12894-021-00852-1. BMC Urol. 2021. PMID: 34016097 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA long intergenic non-coding 00641 mediates cell progression with stimulating cisplatin-resistance in osteosarcoma cells via microRNA-320d/myeloid cell leukemia-1 axis.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):7238-7252. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2045090. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35266447 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA XLOC_006786 inhibits the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells through NOTCH3 signaling pathway by targeting miR-491-5p.Hum Cell. 2023 Nov;36(6):2140-2151. doi: 10.1007/s13577-023-00958-8. Epub 2023 Aug 13. Hum Cell. 2023. PMID: 37573513
-
Targeting Autophagy Using Long Non-Coding RNAs (LncRNAs): New Landscapes in the Arena of Cancer Therapeutics.Cells. 2023 Mar 6;12(5):810. doi: 10.3390/cells12050810. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36899946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LINC00662 Long Non-Coding RNA Knockdown Attenuates the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Osteosarcoma Cells by Regulating the microRNA-15a-5p/Notch2 Axis.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Aug 10;13:7517-7530. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S256464. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32848412 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

